Zbernica i2c: PCF8574: Rozdiel medzi revíziami
Zo stránky SensorWiki
Bez shrnutí editace |
Bez shrnutí editace Značka: manuálne vrátenie |
||
| (38 medziľahlých úprav od 2 ďalších používateľov nie je zobrazených) | |||
| Riadok 1: | Riadok 1: | ||
Záverečný projekt predmetu MIPS / LS2025 - '''Kamil Hanišák''' | |||
Záverečný projekt predmetu MIPS / | |||
== Zadanie == | == Zadanie == | ||
Cieľom zadania bolo vytvoriť jednoduchý mikroprocesorový obvod, ktorý umožňuje ovládať viacero LED diód pomocou i2c expanzného obvodu PCF8574, a naprogramovať jednoduchú svetelnú animáciu. | |||
[[Obrázok:ard.jpg|400px|thumb|center|Vývojová doska ACROB.]] | [[Obrázok:ard.jpg|400px|thumb|center|Vývojová doska ACROB.]] | ||
'''Literatúra:''' | '''Literatúra:''' | ||
* [ | * [https://senzor.robotika.sk/sensorwiki/index.php/Acrob_technical_description Dokumentácia k doske Acrob] | ||
* [ | * [https://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/pcf8574.pdf Dokumentácia ku Zbernici i2c: PCF8574] | ||
| Riadok 20: | Riadok 17: | ||
== Analýza a opis riešenia == | == Analýza a opis riešenia == | ||
Na riešenie zadania sme použili zbernicu i2c PCF8574, ktorá nám umožnila ovládať viacero LED diód pomocou len dvoch vodičov – SDA a SCL. Tento čip komunikuje po i2c zbernici s mikrokontrolérom Arduino Acrob s ATmega328P, pričom každý jej výstupný pin možno samostatne nastavovať na logickú 0 alebo 1. | |||
'''Použité komponenty:''' | |||
* PCF8574P – i2c expander s 8 výstupmi | |||
* 4x LED dióda | |||
* 4x rezistor 220 Ω – ochranné rezistory pred LED diódami | |||
* 2x rezistor 4.7 kΩ – pull-up rezistory na i2c vodiče (SDA a SCL) | |||
* Prepojovacie vodiče a nepájivé pole (breadboard) | |||
[[Súbor:KonfiguraciaPinov.jpeg|250px|thumb|center|Konfigurácia pinov PCF8574P.]] | |||
Naše konkrétne pripojenie pinov čipu PCF8574 k Arduinu a LED diódam: | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! Pin PCF8574 !! Pripojenie | |||
|- | |||
| A0 || Adresovací pin – pripojený na GND | |||
|- | |||
| A1 || Adresovací pin – pripojený na GND | |||
|- | |||
| A2 || Adresovací pin – pripojený na GND | |||
|- | |||
| P0 || Výstup pre LED 1 | |||
|- | |||
| P1 || Výstup pre LED 2 | |||
|- | |||
| P2 || Výstup pre LED 3 | |||
|- | |||
| P3 || Výstup pre LED 4 | |||
|- | |||
| VSS || GND | |||
|- | |||
| P4–P7 || Nepoužité | |||
|- | |||
| INT || Nepripojené (nepoužili sme prerušenie) | |||
|- | |||
| SCL (pin 14) || Pripojené na Arduino A5 + pull-up rezistor na VCC | |||
|- | |||
| SDA (pin 15) || Pripojené na Arduino A4 + pull-up rezistor na VCC | |||
|- | |||
| VDD || Napájanie +5V | |||
|} | |||
'''Schéma zapojenia:''' | |||
[[Súbor: | [[Súbor:Pcf8574.jpeg|400px|thumb|center|Schéma zapojenia.]] | ||
=== Algoritmus a program === | === Algoritmus a program === | ||
Základom programu je cyklické zapínanie a vypínanie jednotlivých výstupov čipu PCF8574 tak, aby vytvorili jednoduchú svetelnú animáciu – postupné rozsvietenie, zhasínanie, bežiace svetlo a spoločné blikanie. | |||
Pri písaní kódu sme využili knižnice i2cmaster.h a i2cmaster.c z cvičení. | |||
'''Použité funkcie:''' | |||
* i2c_init() - Inicializuje i2c zbernicu. Táto funkcia je súčasťou knižnice i2cmaster.h. | |||
* pcf_write(uint8_t data) - Pomocná funkcia, ktorá zabezpečuje zápis jedného bajtu do PCF8574. | |||
* i2c_start(addr)/i2c_write(data)/i2c_stop() - Funkcie z i2cmaster.h pre riadenie zbernice i2c – začatie komunikácie, odoslanie dát, ukončenie prenosu. | |||
* _delay_ms(x) - Časové oneskorenie na vytvorenie vizuálne vnímateľnej animácie LED. | |||
'''Priebeh algoritmu:''' | |||
* Postupné rozsvietenie LED 1 → LED 4 | |||
* Postupné zhasínanie LED 4 → LED 1 | |||
* Bežiace svetlo tam a späť | |||
* Tri spoločné záblesky všetkých LED naraz | |||
<tabs> | <tabs> | ||
<tab name="AVR C-code">< | <tab name="AVR C-code"><syntaxhighlight lang="c++" style="background: LightYellow;"> | ||
#include <avr/io.h> | #include <avr/io.h> | ||
#include <util/delay.h> | |||
#include "i2cmaster.h" | |||
#define PCF8574_ADDR 0x40 | |||
void pcf_write(uint8_t data) { | |||
i2c_start(PCF8574_ADDR + I2C_WRITE); | |||
i2c_write(data); | |||
i2c_stop(); | |||
} | |||
int main(void) | int main(void) { | ||
{ | i2c_init(); | ||
uint8_t stav = 0xFF; // Výstupné bity (všetky LED zhasnuté – log. 1) | |||
while (1) { | |||
// 1. Postupné rozsvietenie LED | |||
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 4; i++) { | |||
stav &= ~(1 << i); // nastav bit i na 0, zapni LED | |||
pcf_write(stav); | |||
_delay_ms(200); | |||
} | |||
// 2. Postupné zhasínanie LED | |||
for (int8_t i = 3; i >= 0; i--) { | |||
stav |= (1 << i); // nastav bit i na 1, zhasni LED | |||
pcf_write(stav); | |||
_delay_ms(200); | |||
} | |||
// 3. Bežiace svetlo tam a späť | |||
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 4; i++) { | |||
pcf_write(~(1 << i)); // iba jeden bit je 0 | |||
_delay_ms(150); | |||
} | |||
for (int8_t i = 2; i >= 1; i--) { | |||
pcf_write(~(1 << i)); | |||
_delay_ms(150); | |||
} | |||
// 4. Všetky LED bliknú naraz 3x | |||
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 3; i++) { | |||
pcf_write(0b11110000); //všetky zapnuté | |||
_delay_ms(150); | |||
pcf_write(0xFF); //všetky vypnuté | |||
_delay_ms(150); | |||
} | |||
_delay_ms(500); // pauza medzi cyklami | |||
} | |||
} | } | ||
</ | |||
<tab name=" | </syntaxhighlight ></tab> | ||
<tab name="i2cmaster.h"><syntaxhighlight lang="c++" style="background: LightYellow;"> | |||
#ifndef _I2CMASTER_H | |||
#define _I2CMASTER_H | |||
/************************************************************************* | |||
* Title: C include file for the I2C master interface | |||
* (i2cmaster.S or twimaster.c) | |||
* Author: Peter Fleury <pfleury@gmx.ch> | |||
* File: $Id: i2cmaster.h,v 1.12 2015/09/16 09:27:58 peter Exp $ | |||
* Software: AVR-GCC 4.x | |||
* Target: any AVR device | |||
* Usage: see Doxygen manual | |||
**************************************************************************/ | |||
/** | |||
@file | |||
@defgroup pfleury_ic2master I2C Master library | |||
@code #include <i2cmaster.h> @endcode | |||
@brief I2C (TWI) Master Software Library | |||
Basic routines for communicating with I2C slave devices. This single master | |||
implementation is limited to one bus master on the I2C bus. | |||
This I2c library is implemented as a compact assembler software implementation of the I2C protocol | |||
which runs on any AVR (i2cmaster.S) and as a TWI hardware interface for all AVR with built-in TWI hardware (twimaster.c). | |||
Since the API for these two implementations is exactly the same, an application can be linked either against the | |||
software I2C implementation or the hardware I2C implementation. | |||
Use 4.7k pull-up resistor on the SDA and SCL pin. | |||
Adapt the SCL and SDA port and pin definitions and eventually the delay routine in the module | |||
i2cmaster.S to your target when using the software I2C implementation ! | |||
Adjust the CPU clock frequence F_CPU in twimaster.c or in the Makfile when using the TWI hardware implementaion. | |||
@note | |||
The module i2cmaster.S is based on the Atmel Application Note AVR300, corrected and adapted | |||
to GNU assembler and AVR-GCC C call interface. | |||
Replaced the incorrect quarter period delays found in AVR300 with | |||
half period delays. | |||
@author Peter Fleury pfleury@gmx.ch http://tinyurl.com/peterfleury | |||
@copyright (C) 2015 Peter Fleury, GNU General Public License Version 3 | |||
@par API Usage Example | |||
The following code shows typical usage of this library, see example test_i2cmaster.c | |||
@code | |||
#include <i2cmaster.h> | |||
#define Dev24C02 0xA2 // device address of EEPROM 24C02, see datasheet | |||
int main(void) | |||
{ | |||
unsigned char ret; | |||
i2c_init(); // initialize I2C library | |||
// write 0x75 to EEPROM address 5 (Byte Write) | |||
i2c_start_wait(Dev24C02+I2C_WRITE); // set device address and write mode | |||
i2c_write(0x05); // write address = 5 | |||
i2c_write(0x75); // write value 0x75 to EEPROM | |||
i2c_stop(); // set stop conditon = release bus | |||
// read previously written value back from EEPROM address 5 | |||
i2c_start_wait(Dev24C02+I2C_WRITE); // set device address and write mode | |||
i2c_write(0x05); // write address = 5 | |||
i2c_rep_start(Dev24C02+I2C_READ); // set device address and read mode | |||
ret = i2c_readNak(); // read one byte from EEPROM | |||
i2c_stop(); | |||
for(;;); | |||
} | |||
@endcode | |||
*/ | |||
/**@{*/ | |||
#if (__GNUC__ * 100 + __GNUC_MINOR__) < 304 | |||
#error "This library requires AVR-GCC 3.4 or later, update to newer AVR-GCC compiler !" | |||
#endif | |||
#include <avr/io.h> | #include <avr/io.h> | ||
void | /** defines the data direction (reading from I2C device) in i2c_start(),i2c_rep_start() */ | ||
#define I2C_READ 1 | |||
/** defines the data direction (writing to I2C device) in i2c_start(),i2c_rep_start() */ | |||
#define I2C_WRITE 0 | |||
/** | |||
@brief initialize the I2C master interace. Need to be called only once | |||
@return none | |||
*/ | |||
extern void i2c_init(void); | |||
/** | |||
@brief Terminates the data transfer and releases the I2C bus | |||
@return none | |||
*/ | |||
extern void i2c_stop(void); | |||
/** | |||
@brief Issues a start condition and sends address and transfer direction | |||
@param addr address and transfer direction of I2C device | |||
@retval 0 device accessible | |||
@retval 1 failed to access device | |||
*/ | |||
extern unsigned char i2c_start(unsigned char addr); | |||
/** | |||
@brief Issues a repeated start condition and sends address and transfer direction | |||
@param addr address and transfer direction of I2C device | |||
@retval 0 device accessible | |||
@retval 1 failed to access device | |||
*/ | |||
extern unsigned char i2c_rep_start(unsigned char addr); | |||
/** | |||
@brief Issues a start condition and sends address and transfer direction | |||
If device is busy, use ack polling to wait until device ready | |||
@param addr address and transfer direction of I2C device | |||
@return none | |||
*/ | |||
extern void i2c_start_wait(unsigned char addr); | |||
/** | |||
@brief Send one byte to I2C device | |||
@param data byte to be transfered | |||
@retval 0 write successful | |||
@retval 1 write failed | |||
*/ | |||
extern unsigned char i2c_write(unsigned char data); | |||
unsigned | /** | ||
</ | @brief read one byte from the I2C device, request more data from device | ||
@return byte read from I2C device | |||
*/ | |||
extern unsigned char i2c_readAck(void); | |||
/** | |||
@brief read one byte from the I2C device, read is followed by a stop condition | |||
@return byte read from I2C device | |||
*/ | |||
extern unsigned char i2c_readNak(void); | |||
/** | |||
@brief read one byte from the I2C device | |||
Implemented as a macro, which calls either @ref i2c_readAck or @ref i2c_readNak | |||
@param ack 1 send ack, request more data from device<br> | |||
0 send nak, read is followed by a stop condition | |||
@return byte read from I2C device | |||
*/ | |||
extern unsigned char i2c_read(unsigned char ack); | |||
#define i2c_read(ack) (ack) ? i2c_readAck() : i2c_readNak(); | |||
/**@}*/ | |||
#endif | |||
</syntaxhighlight ></tab> | |||
<tab name="i2cmaster.c"><syntaxhighlight lang="c++" style="background: LightYellow;"> | |||
/************************************************************************* | |||
* Title: I2C master library using hardware TWI interface | |||
* Author: Peter Fleury <pfleury@gmx.ch> http://jump.to/fleury | |||
* File: $Id: twimaster.c,v 1.4 2015/01/17 12:16:05 peter Exp $ | |||
* Software: AVR-GCC 3.4.3 / avr-libc 1.2.3 | |||
* Target: any AVR device with hardware TWI | |||
* Usage: API compatible with I2C Software Library i2cmaster.h | |||
**************************************************************************/ | |||
#include <inttypes.h> | |||
#include <compat/twi.h> | |||
#include "i2cmaster.h" | |||
/* define CPU frequency in hz here if not defined in Makefile */ | |||
#ifndef F_CPU | |||
#define F_CPU 16000000UL | |||
#endif | |||
/* I2C clock in Hz */ | |||
#define SCL_CLOCK 100000L | |||
/************************************************************************* | |||
Initialization of the I2C bus interface. Need to be called only once | |||
*************************************************************************/ | |||
void i2c_init(void) | |||
{ | |||
/* initialize TWI clock: 100 kHz clock, TWPS = 0 => prescaler = 1 */ | |||
TWSR = 0; /* no prescaler */ | |||
TWBR = ((F_CPU/SCL_CLOCK)-16)/2; /* must be > 10 for stable operation */ | |||
}/* i2c_init */ | |||
/************************************************************************* | |||
Issues a start condition and sends address and transfer direction. | |||
return 0 = device accessible, 1= failed to access device | |||
*************************************************************************/ | |||
unsigned char i2c_start(unsigned char address) | |||
{ | |||
uint8_t twst; | |||
// send START condition | |||
TWCR = (1<<TWINT) | (1<<TWSTA) | (1<<TWEN); | |||
// wait until transmission completed | |||
while(!(TWCR & (1<<TWINT))); | |||
// check value of TWI Status Register. Mask prescaler bits. | |||
twst = TW_STATUS & 0xF8; | |||
if ( (twst != TW_START) && (twst != TW_REP_START)) return 1; | |||
// send device address | |||
TWDR = address; | |||
TWCR = (1<<TWINT) | (1<<TWEN); | |||
// wail until transmission completed and ACK/NACK has been received | |||
while(!(TWCR & (1<<TWINT))); | |||
// check value of TWI Status Register. Mask prescaler bits. | |||
twst = TW_STATUS & 0xF8; | |||
if ( (twst != TW_MT_SLA_ACK) && (twst != TW_MR_SLA_ACK) ) return 1; | |||
return 0; | |||
}/* i2c_start */ | |||
/************************************************************************* | |||
Issues a start condition and sends address and transfer direction. | |||
If device is busy, use ack polling to wait until device is ready | |||
Input: address and transfer direction of I2C device | |||
*************************************************************************/ | |||
void i2c_start_wait(unsigned char address) | |||
{ | |||
uint8_t twst; | |||
while ( 1 ) | |||
{ | |||
// send START condition | |||
TWCR = (1<<TWINT) | (1<<TWSTA) | (1<<TWEN); | |||
// wait until transmission completed | |||
while(!(TWCR & (1<<TWINT))); | |||
// check value of TWI Status Register. Mask prescaler bits. | |||
twst = TW_STATUS & 0xF8; | |||
if ( (twst != TW_START) && (twst != TW_REP_START)) continue; | |||
// send device address | |||
TWDR = address; | |||
TWCR = (1<<TWINT) | (1<<TWEN); | |||
// wail until transmission completed | |||
while(!(TWCR & (1<<TWINT))); | |||
// check value of TWI Status Register. Mask prescaler bits. | |||
twst = TW_STATUS & 0xF8; | |||
if ( (twst == TW_MT_SLA_NACK )||(twst ==TW_MR_DATA_NACK) ) | |||
{ | |||
/* device busy, send stop condition to terminate write operation */ | |||
TWCR = (1<<TWINT) | (1<<TWEN) | (1<<TWSTO); | |||
// wait until stop condition is executed and bus released | |||
while(TWCR & (1<<TWSTO)); | |||
continue; | |||
} | |||
//if( twst != TW_MT_SLA_ACK) return 1; | |||
break; | |||
} | |||
}/* i2c_start_wait */ | |||
/************************************************************************* | |||
Issues a repeated start condition and sends address and transfer direction | |||
Input: address and transfer direction of I2C device | |||
Return: 0 device accessible | |||
1 failed to access device | |||
*************************************************************************/ | |||
unsigned char i2c_rep_start(unsigned char address) | |||
{ | |||
return i2c_start( address ); | |||
}/* i2c_rep_start */ | |||
/************************************************************************* | |||
Terminates the data transfer and releases the I2C bus | |||
*************************************************************************/ | |||
void i2c_stop(void) | |||
{ | |||
/* send stop condition */ | |||
TWCR = (1<<TWINT) | (1<<TWEN) | (1<<TWSTO); | |||
// wait until stop condition is executed and bus released | |||
while(TWCR & (1<<TWSTO)); | |||
}/* i2c_stop */ | |||
/************************************************************************* | |||
Send one byte to I2C device | |||
Input: byte to be transfered | |||
Return: 0 write successful | |||
1 write failed | |||
*************************************************************************/ | |||
unsigned char i2c_write( unsigned char data ) | |||
{ | |||
uint8_t twst; | |||
// send data to the previously addressed device | |||
TWDR = data; | |||
TWCR = (1<<TWINT) | (1<<TWEN); | |||
// wait until transmission completed | |||
while(!(TWCR & (1<<TWINT))); | |||
// check value of TWI Status Register. Mask prescaler bits | |||
twst = TW_STATUS & 0xF8; | |||
if( twst != TW_MT_DATA_ACK) return 1; | |||
return 0; | |||
}/* i2c_write */ | |||
/************************************************************************* | |||
Read one byte from the I2C device, request more data from device | |||
Return: byte read from I2C device | |||
*************************************************************************/ | |||
unsigned char i2c_readAck(void) | |||
{ | |||
TWCR = (1<<TWINT) | (1<<TWEN) | (1<<TWEA); | |||
while(!(TWCR & (1<<TWINT))); | |||
return TWDR; | |||
}/* i2c_readAck */ | |||
/************************************************************************* | |||
Read one byte from the I2C device, read is followed by a stop condition | |||
Return: byte read from I2C device | |||
*************************************************************************/ | |||
unsigned char i2c_readNak(void) | |||
{ | |||
TWCR = (1<<TWINT) | (1<<TWEN); | |||
while(!(TWCR & (1<<TWINT))); | |||
return TWDR; | |||
}/* i2c_readNak */ | |||
</syntaxhighlight ></tab> | |||
</tabs> | </tabs> | ||
Zdrojový kód: [[Médiá:ProjektKamilHanišák.zip|ProjektKamilHanišák.zip]] | |||
=== Overenie === | === Overenie === | ||
Funkčnosť nášho riešenia sme overili vizuálne, a to pozorovaním LED animácie, ktorá prebiehala podľa očakávaného správania definovaného v napísanom kóde. | |||
[[Súbor: | [[Súbor:ObvodZapojenia.jpeg|400px|thumb|center|Obvod zapojenia.]] | ||
'''Video:''' | '''Video:''' | ||
<center><youtube> | <center><youtube>_lIVN4c37R4</youtube></center> | ||
Kľúčové slová 'Category', ktoré sú na konci stránky nemeňte. | Kľúčové slová 'Category', ktoré sú na konci stránky nemeňte. | ||
[[Category:AVR]] [[Category:MIPS]] | [[Category:AVR]] [[Category:MIPS]] | ||
Aktuálna revízia z 21:27, 7. september 2025
Záverečný projekt predmetu MIPS / LS2025 - Kamil Hanišák
Zadanie
Cieľom zadania bolo vytvoriť jednoduchý mikroprocesorový obvod, ktorý umožňuje ovládať viacero LED diód pomocou i2c expanzného obvodu PCF8574, a naprogramovať jednoduchú svetelnú animáciu.
Literatúra:
Analýza a opis riešenia
Na riešenie zadania sme použili zbernicu i2c PCF8574, ktorá nám umožnila ovládať viacero LED diód pomocou len dvoch vodičov – SDA a SCL. Tento čip komunikuje po i2c zbernici s mikrokontrolérom Arduino Acrob s ATmega328P, pričom každý jej výstupný pin možno samostatne nastavovať na logickú 0 alebo 1.
Použité komponenty:
- PCF8574P – i2c expander s 8 výstupmi
- 4x LED dióda
- 4x rezistor 220 Ω – ochranné rezistory pred LED diódami
- 2x rezistor 4.7 kΩ – pull-up rezistory na i2c vodiče (SDA a SCL)
- Prepojovacie vodiče a nepájivé pole (breadboard)
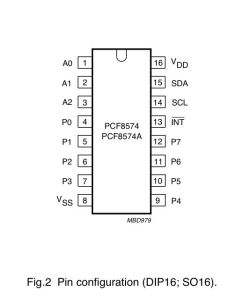
Naše konkrétne pripojenie pinov čipu PCF8574 k Arduinu a LED diódam:
| Pin PCF8574 | Pripojenie |
|---|---|
| A0 | Adresovací pin – pripojený na GND |
| A1 | Adresovací pin – pripojený na GND |
| A2 | Adresovací pin – pripojený na GND |
| P0 | Výstup pre LED 1 |
| P1 | Výstup pre LED 2 |
| P2 | Výstup pre LED 3 |
| P3 | Výstup pre LED 4 |
| VSS | GND |
| P4–P7 | Nepoužité |
| INT | Nepripojené (nepoužili sme prerušenie) |
| SCL (pin 14) | Pripojené na Arduino A5 + pull-up rezistor na VCC |
| SDA (pin 15) | Pripojené na Arduino A4 + pull-up rezistor na VCC |
| VDD | Napájanie +5V |
Schéma zapojenia:
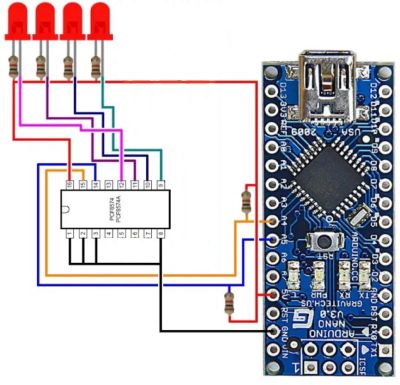
Algoritmus a program
Základom programu je cyklické zapínanie a vypínanie jednotlivých výstupov čipu PCF8574 tak, aby vytvorili jednoduchú svetelnú animáciu – postupné rozsvietenie, zhasínanie, bežiace svetlo a spoločné blikanie. Pri písaní kódu sme využili knižnice i2cmaster.h a i2cmaster.c z cvičení.
Použité funkcie:
- i2c_init() - Inicializuje i2c zbernicu. Táto funkcia je súčasťou knižnice i2cmaster.h.
- pcf_write(uint8_t data) - Pomocná funkcia, ktorá zabezpečuje zápis jedného bajtu do PCF8574.
- i2c_start(addr)/i2c_write(data)/i2c_stop() - Funkcie z i2cmaster.h pre riadenie zbernice i2c – začatie komunikácie, odoslanie dát, ukončenie prenosu.
- _delay_ms(x) - Časové oneskorenie na vytvorenie vizuálne vnímateľnej animácie LED.
Priebeh algoritmu:
- Postupné rozsvietenie LED 1 → LED 4
- Postupné zhasínanie LED 4 → LED 1
- Bežiace svetlo tam a späť
- Tri spoločné záblesky všetkých LED naraz
#include <avr/io.h>
#include <util/delay.h>
#include "i2cmaster.h"
#define PCF8574_ADDR 0x40
void pcf_write(uint8_t data) {
i2c_start(PCF8574_ADDR + I2C_WRITE);
i2c_write(data);
i2c_stop();
}
int main(void) {
i2c_init();
uint8_t stav = 0xFF; // Výstupné bity (všetky LED zhasnuté – log. 1)
while (1) {
// 1. Postupné rozsvietenie LED
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
stav &= ~(1 << i); // nastav bit i na 0, zapni LED
pcf_write(stav);
_delay_ms(200);
}
// 2. Postupné zhasínanie LED
for (int8_t i = 3; i >= 0; i--) {
stav |= (1 << i); // nastav bit i na 1, zhasni LED
pcf_write(stav);
_delay_ms(200);
}
// 3. Bežiace svetlo tam a späť
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
pcf_write(~(1 << i)); // iba jeden bit je 0
_delay_ms(150);
}
for (int8_t i = 2; i >= 1; i--) {
pcf_write(~(1 << i));
_delay_ms(150);
}
// 4. Všetky LED bliknú naraz 3x
for (uint8_t i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
pcf_write(0b11110000); //všetky zapnuté
_delay_ms(150);
pcf_write(0xFF); //všetky vypnuté
_delay_ms(150);
}
_delay_ms(500); // pauza medzi cyklami
}
}
#ifndef _I2CMASTER_H
#define _I2CMASTER_H
/*************************************************************************
* Title: C include file for the I2C master interface
* (i2cmaster.S or twimaster.c)
* Author: Peter Fleury <pfleury@gmx.ch>
* File: $Id: i2cmaster.h,v 1.12 2015/09/16 09:27:58 peter Exp $
* Software: AVR-GCC 4.x
* Target: any AVR device
* Usage: see Doxygen manual
**************************************************************************/
/**
@file
@defgroup pfleury_ic2master I2C Master library
@code #include <i2cmaster.h> @endcode
@brief I2C (TWI) Master Software Library
Basic routines for communicating with I2C slave devices. This single master
implementation is limited to one bus master on the I2C bus.
This I2c library is implemented as a compact assembler software implementation of the I2C protocol
which runs on any AVR (i2cmaster.S) and as a TWI hardware interface for all AVR with built-in TWI hardware (twimaster.c).
Since the API for these two implementations is exactly the same, an application can be linked either against the
software I2C implementation or the hardware I2C implementation.
Use 4.7k pull-up resistor on the SDA and SCL pin.
Adapt the SCL and SDA port and pin definitions and eventually the delay routine in the module
i2cmaster.S to your target when using the software I2C implementation !
Adjust the CPU clock frequence F_CPU in twimaster.c or in the Makfile when using the TWI hardware implementaion.
@note
The module i2cmaster.S is based on the Atmel Application Note AVR300, corrected and adapted
to GNU assembler and AVR-GCC C call interface.
Replaced the incorrect quarter period delays found in AVR300 with
half period delays.
@author Peter Fleury pfleury@gmx.ch http://tinyurl.com/peterfleury
@copyright (C) 2015 Peter Fleury, GNU General Public License Version 3
@par API Usage Example
The following code shows typical usage of this library, see example test_i2cmaster.c
@code
#include <i2cmaster.h>
#define Dev24C02 0xA2 // device address of EEPROM 24C02, see datasheet
int main(void)
{
unsigned char ret;
i2c_init(); // initialize I2C library
// write 0x75 to EEPROM address 5 (Byte Write)
i2c_start_wait(Dev24C02+I2C_WRITE); // set device address and write mode
i2c_write(0x05); // write address = 5
i2c_write(0x75); // write value 0x75 to EEPROM
i2c_stop(); // set stop conditon = release bus
// read previously written value back from EEPROM address 5
i2c_start_wait(Dev24C02+I2C_WRITE); // set device address and write mode
i2c_write(0x05); // write address = 5
i2c_rep_start(Dev24C02+I2C_READ); // set device address and read mode
ret = i2c_readNak(); // read one byte from EEPROM
i2c_stop();
for(;;);
}
@endcode
*/
/**@{*/
#if (__GNUC__ * 100 + __GNUC_MINOR__) < 304
#error "This library requires AVR-GCC 3.4 or later, update to newer AVR-GCC compiler !"
#endif
#include <avr/io.h>
/** defines the data direction (reading from I2C device) in i2c_start(),i2c_rep_start() */
#define I2C_READ 1
/** defines the data direction (writing to I2C device) in i2c_start(),i2c_rep_start() */
#define I2C_WRITE 0
/**
@brief initialize the I2C master interace. Need to be called only once
@return none
*/
extern void i2c_init(void);
/**
@brief Terminates the data transfer and releases the I2C bus
@return none
*/
extern void i2c_stop(void);
/**
@brief Issues a start condition and sends address and transfer direction
@param addr address and transfer direction of I2C device
@retval 0 device accessible
@retval 1 failed to access device
*/
extern unsigned char i2c_start(unsigned char addr);
/**
@brief Issues a repeated start condition and sends address and transfer direction
@param addr address and transfer direction of I2C device
@retval 0 device accessible
@retval 1 failed to access device
*/
extern unsigned char i2c_rep_start(unsigned char addr);
/**
@brief Issues a start condition and sends address and transfer direction
If device is busy, use ack polling to wait until device ready
@param addr address and transfer direction of I2C device
@return none
*/
extern void i2c_start_wait(unsigned char addr);
/**
@brief Send one byte to I2C device
@param data byte to be transfered
@retval 0 write successful
@retval 1 write failed
*/
extern unsigned char i2c_write(unsigned char data);
/**
@brief read one byte from the I2C device, request more data from device
@return byte read from I2C device
*/
extern unsigned char i2c_readAck(void);
/**
@brief read one byte from the I2C device, read is followed by a stop condition
@return byte read from I2C device
*/
extern unsigned char i2c_readNak(void);
/**
@brief read one byte from the I2C device
Implemented as a macro, which calls either @ref i2c_readAck or @ref i2c_readNak
@param ack 1 send ack, request more data from device<br>
0 send nak, read is followed by a stop condition
@return byte read from I2C device
*/
extern unsigned char i2c_read(unsigned char ack);
#define i2c_read(ack) (ack) ? i2c_readAck() : i2c_readNak();
/**@}*/
#endif
/*************************************************************************
* Title: I2C master library using hardware TWI interface
* Author: Peter Fleury <pfleury@gmx.ch> http://jump.to/fleury
* File: $Id: twimaster.c,v 1.4 2015/01/17 12:16:05 peter Exp $
* Software: AVR-GCC 3.4.3 / avr-libc 1.2.3
* Target: any AVR device with hardware TWI
* Usage: API compatible with I2C Software Library i2cmaster.h
**************************************************************************/
#include <inttypes.h>
#include <compat/twi.h>
#include "i2cmaster.h"
/* define CPU frequency in hz here if not defined in Makefile */
#ifndef F_CPU
#define F_CPU 16000000UL
#endif
/* I2C clock in Hz */
#define SCL_CLOCK 100000L
/*************************************************************************
Initialization of the I2C bus interface. Need to be called only once
*************************************************************************/
void i2c_init(void)
{
/* initialize TWI clock: 100 kHz clock, TWPS = 0 => prescaler = 1 */
TWSR = 0; /* no prescaler */
TWBR = ((F_CPU/SCL_CLOCK)-16)/2; /* must be > 10 for stable operation */
}/* i2c_init */
/*************************************************************************
Issues a start condition and sends address and transfer direction.
return 0 = device accessible, 1= failed to access device
*************************************************************************/
unsigned char i2c_start(unsigned char address)
{
uint8_t twst;
// send START condition
TWCR = (1<<TWINT) | (1<<TWSTA) | (1<<TWEN);
// wait until transmission completed
while(!(TWCR & (1<<TWINT)));
// check value of TWI Status Register. Mask prescaler bits.
twst = TW_STATUS & 0xF8;
if ( (twst != TW_START) && (twst != TW_REP_START)) return 1;
// send device address
TWDR = address;
TWCR = (1<<TWINT) | (1<<TWEN);
// wail until transmission completed and ACK/NACK has been received
while(!(TWCR & (1<<TWINT)));
// check value of TWI Status Register. Mask prescaler bits.
twst = TW_STATUS & 0xF8;
if ( (twst != TW_MT_SLA_ACK) && (twst != TW_MR_SLA_ACK) ) return 1;
return 0;
}/* i2c_start */
/*************************************************************************
Issues a start condition and sends address and transfer direction.
If device is busy, use ack polling to wait until device is ready
Input: address and transfer direction of I2C device
*************************************************************************/
void i2c_start_wait(unsigned char address)
{
uint8_t twst;
while ( 1 )
{
// send START condition
TWCR = (1<<TWINT) | (1<<TWSTA) | (1<<TWEN);
// wait until transmission completed
while(!(TWCR & (1<<TWINT)));
// check value of TWI Status Register. Mask prescaler bits.
twst = TW_STATUS & 0xF8;
if ( (twst != TW_START) && (twst != TW_REP_START)) continue;
// send device address
TWDR = address;
TWCR = (1<<TWINT) | (1<<TWEN);
// wail until transmission completed
while(!(TWCR & (1<<TWINT)));
// check value of TWI Status Register. Mask prescaler bits.
twst = TW_STATUS & 0xF8;
if ( (twst == TW_MT_SLA_NACK )||(twst ==TW_MR_DATA_NACK) )
{
/* device busy, send stop condition to terminate write operation */
TWCR = (1<<TWINT) | (1<<TWEN) | (1<<TWSTO);
// wait until stop condition is executed and bus released
while(TWCR & (1<<TWSTO));
continue;
}
//if( twst != TW_MT_SLA_ACK) return 1;
break;
}
}/* i2c_start_wait */
/*************************************************************************
Issues a repeated start condition and sends address and transfer direction
Input: address and transfer direction of I2C device
Return: 0 device accessible
1 failed to access device
*************************************************************************/
unsigned char i2c_rep_start(unsigned char address)
{
return i2c_start( address );
}/* i2c_rep_start */
/*************************************************************************
Terminates the data transfer and releases the I2C bus
*************************************************************************/
void i2c_stop(void)
{
/* send stop condition */
TWCR = (1<<TWINT) | (1<<TWEN) | (1<<TWSTO);
// wait until stop condition is executed and bus released
while(TWCR & (1<<TWSTO));
}/* i2c_stop */
/*************************************************************************
Send one byte to I2C device
Input: byte to be transfered
Return: 0 write successful
1 write failed
*************************************************************************/
unsigned char i2c_write( unsigned char data )
{
uint8_t twst;
// send data to the previously addressed device
TWDR = data;
TWCR = (1<<TWINT) | (1<<TWEN);
// wait until transmission completed
while(!(TWCR & (1<<TWINT)));
// check value of TWI Status Register. Mask prescaler bits
twst = TW_STATUS & 0xF8;
if( twst != TW_MT_DATA_ACK) return 1;
return 0;
}/* i2c_write */
/*************************************************************************
Read one byte from the I2C device, request more data from device
Return: byte read from I2C device
*************************************************************************/
unsigned char i2c_readAck(void)
{
TWCR = (1<<TWINT) | (1<<TWEN) | (1<<TWEA);
while(!(TWCR & (1<<TWINT)));
return TWDR;
}/* i2c_readAck */
/*************************************************************************
Read one byte from the I2C device, read is followed by a stop condition
Return: byte read from I2C device
*************************************************************************/
unsigned char i2c_readNak(void)
{
TWCR = (1<<TWINT) | (1<<TWEN);
while(!(TWCR & (1<<TWINT)));
return TWDR;
}/* i2c_readNak */
Zdrojový kód: ProjektKamilHanišák.zip
Overenie
Funkčnosť nášho riešenia sme overili vizuálne, a to pozorovaním LED animácie, ktorá prebiehala podľa očakávaného správania definovaného v napísanom kóde.
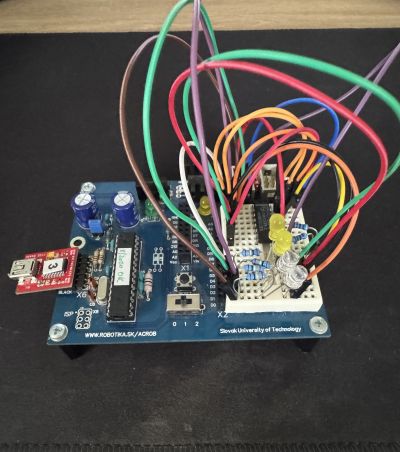
Video:
Kľúčové slová 'Category', ktoré sú na konci stránky nemeňte.