Acrob043
Zo stránky SensorWiki
Software for Color Sensors
1. Basic demonstration
- TCS230 sensor: BASIC Stamp II code
- ColorPAL sensor Arduino code
2. Color Matching Demo software
Following Arduino code works with an original Parallax (or PhiPi) ColorDemo.exe program available at the following address: http://www.parallax.com/Portals/0/Downloads/docs/prod/sens/ColorPAL_programs.zip
- TCS230 sensor: BASIC Stamp II code
- ColorPAL sensor Arduino code
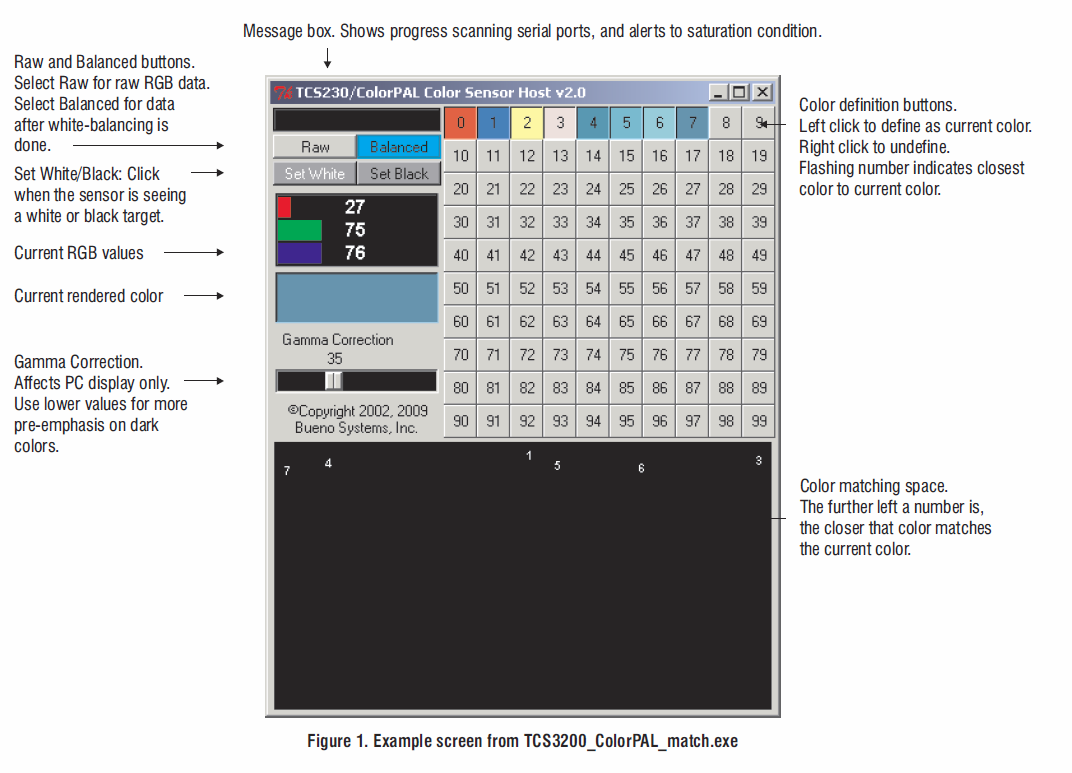
4. Calculations
Color matching is done using a "minimax" approach in the RGB color space. In this method, the distance between two colors is the absolute value of the difference between the RGB component that differs most:
Di = max{|R - Ri|, |G - Gi|, |B - Bi|}
where R, G and B are the red, green, and blue coordinates of the color being scanned; and Ri, Gi and Bi are the coordinates of stored color. The color with the closest match is taken to be the one whose is the smallest, i.e. minimizing the maximum difference. Hence the term "minimax".
3. Processing software
- PC software: Processing code
- TCS230 sensor: BASIC Stamp II code
- ColorPAL sensor Arduino code
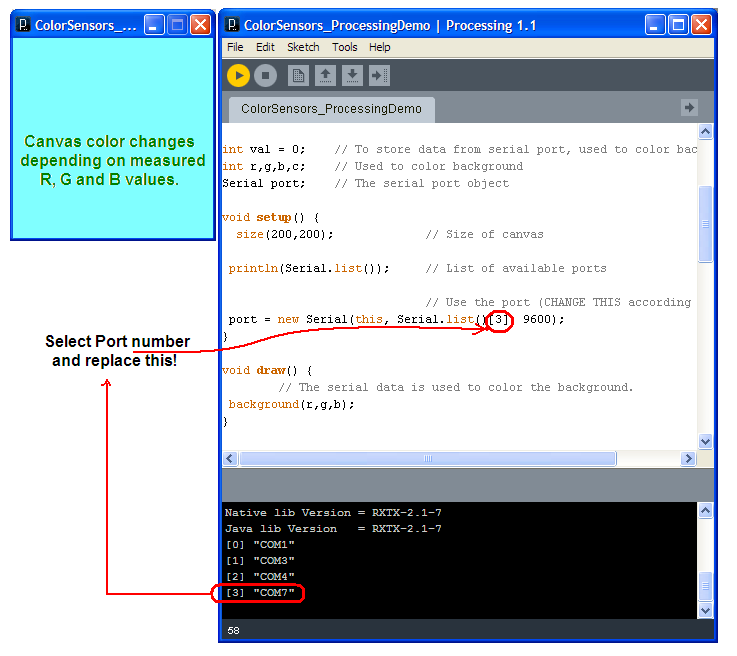
// Demonstration program for Color Sensors
// TCS 230 sensor requires TCS230_Demo03_SS_CIM.bs2
// ColorPAL sensor requires ColorPAL_Demo03_SS_CIM.ino with line 78 uncommented
//
// SS_CIM 2013
// Richard Balogh
import processing.serial.*;
int lf = 10; // Line Feed in ASCII
int cr = 13; // Carriage Returin in ASCII
int val = 0; // To store data from serial port, used to color background
int r,g,b,c; // Used to color background
Serial port; // The serial port object
void setup() {
size(200,200); // Size of canvas
println(Serial.list()); // List of available ports
// Use the port (CHANGE THIS according YOUR PC!)
port = new Serial(this, Serial.list()[3], 9600);
}
void draw() {
// The serial data is used to color the background.
background(r,g,b);
}
// Called whenever there is something available to read
void serialEvent(Serial port) {
// Data from the Serial port is read in serialEvent()
// using the readStringUntil() function with LF as
// the end character.
String input = port.readStringUntil(lf);
if (input != null) {
// Print message received
println( "Receiving:" + input);
// The data is split into an array of Strings with
// a comma as a delimiter and converted into an
// array of integers.
int[] vals = int(splitTokens(input, ","));
// Fill r,g,b variables
r = vals[0];
g = vals[1];
b = vals[2];
c = vals[3];
/* ************************************* */
/* */
/* Here is place for Your code!!! */
/* */
/* ************************************* */
println( "R:" + r);
println( "G:" + g);
println( "B:" + b);
println( "C:" + c);
}
}