Zbernica i2c: Rozdiel medzi revíziami
Zo stránky SensorWiki
Bez shrnutí editace |
Bez shrnutí editace |
||
| Riadok 50: | Riadok 50: | ||
* Arduino TWI Library https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/Wire | * Arduino TWI Library https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/Wire | ||
* http://playground.arduino.cc/Main/WireLibraryDetailedReference | * http://playground.arduino.cc/Main/WireLibraryDetailedReference | ||
* http://fritzing.org/projects/readwrite-serial-eeprom-via-i2c - DO PPT | |||
* https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/i2c - DO PPT | |||
Verzia z 14:42, 17. marec 2016
| I²C | |
 | |
| Type | Bus |
| Production history | |
|---|---|
| Designer | Philips Semiconductor, known
|
| Designed | 1982; 34 years ago |
| Data | |
| Signal | Open drain |
| Width | 1 bit (SDA) + clock (SCL) |
| Bitrate | 0.1 / 0.4 / 1.0 / 3.4 / 5.0 Mbit/s (depending on mode) |
| Protocol | Serial, Half Duplex |
I²C (Inter-Integrated Circuit), pronounced I-squared-C, is a multi-master, multi-slave, single-ended, serial computer bus invented by Philips Semiconductor (now NXP Semiconductors). It is typically used for attaching lower-speed peripheral ICs to processors and microcontrollers. Alternatively I²C is spelled I2C (pronounced I-two-C) or IIC (pronounced I-I-C).
Since October 10, 2006, no licensing fees are required to implement the I²C protocol. However, fees are still required to obtain I²C slave addresses allocated by NXP.[1]
Several competitors, such as Siemens AG (later Infineon Technologies AG, now Intel mobile communications), NEC, Texas Instruments, STMicroelectronics (formerly SGS-Thomson), Motorola (later Freescale, now merged with NXP[2]), Nordic Semiconductor and Intersil, have introduced compatible I²C products to the market since the mid-1990s.
SMBus, defined by Intel in 1995, is a subset of I²C that defines the protocol use more strictly. One purpose of SMBus is to promote robustness and interoperability. Accordingly, modern I²C systems incorporate some policies and rules from SMBus, sometimes supporting both I²C and SMBus, requiring only minimal reconfiguration either by commanding or output pin use.
Literatúra
- Official I2C Specification Version 6 http://www.nxp.com/documents/user_manual/UM10204.pdf
- Official List of assigned NXP / Philips I2C addresses http://www.diolan.com/downloads/i2c-address-allocation-table.pdf
- Podrobný článok na Wikipedii: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/I%C2%B2C
- Pseudokod bitbang i2c https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/I%C2%B2C#Example_of_bit-banging_the_I.C2.B2C_Master_protocol
- https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/i2c Dobry tutorial
- Procyon SW library http://www.procyonengineering.com/embedded/avr/avrlib/docs/html/i2csw_8c-source.html
- Bitbanging by hand http://hackaday.com/2013/08/11/bitbanging-i2c-by-hand/
- http://hackaday.com/2015/06/25/embed-with-elliot-i2c-bus-scanning/
- http://howtomechatronics.com/tutorials/arduino/how-i2c-communication-works-and-how-to-use-it-with-arduino/
- Arduino TWI Library https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/Wire
- http://playground.arduino.cc/Main/WireLibraryDetailedReference
- http://fritzing.org/projects/readwrite-serial-eeprom-via-i2c - DO PPT
- https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/i2c - DO PPT
- M24C02 Datasheet
- Mitchell Kahn: Programming the i2c interface. Dr. Dobb's Journal, June 1992.
- http://dsscircuits.com/articles/86-articles/47-effects-of-varying-i2c-pull-up-resistors
- http://www.gammon.com.au/i2c
- http://www.gammon.com.au/forum/?id=10896
Datasheets
Vsetko mozne k zbernici i2c (mozno presunut na stranku Category):
Tools
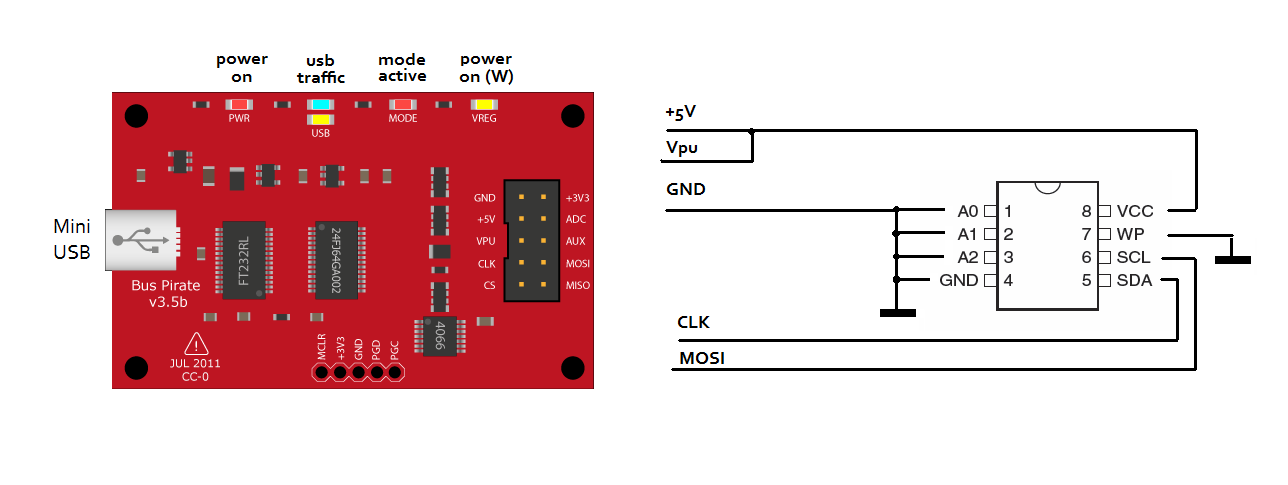
Bus Pirate
Bus Pirate po pripojení sa nainštaluje FTDI serial port driver a OS mu pridelí nejaký port. Cez tento port sa terminálovým programom pripojíme k Bus Piratovi. Parametre portu sú 115 200 bps / 8 / N / 1, no Flow control.
Prvý príkaz je obvykle otáznik, zobrazí sa celé menu.
Postup príkazov pre prácu s i2c zbernicou:
HiZ> ?
MENUS
? Help
I Status info
M Bus mode
B Terminal speed
O Data display format
V Check supply voltages
F Frequency count on AUX
G Frequency generator/PWM on AUX
C AUX pin assignment
L Bit order
P Pullup resistors
= HEX/DEC/BIN converter
~ Self test
# Reset
$ Bootloader
SYNTAX
A/a/@ AUX output toggle H/L/read
W/w Power supply toggle on/off
d (D) Measure voltage on ADC probe (continuous)
[ ({) Start (with read)
] or } Stop
R or r Read byte
0b Write BIN byte
0h or 0x Write HEX byte
0-255 Write DEC byte
, Delimiter (also space)
& 1uS delay
: Repeat (r:2, 0x0a:4, &:20, ^:2, etc.)
(#) Run macro, (0) for macro list
RAW BUS OPERATIONS
/\ Clock H/L
-/_ Data H/L
. Read data input pin state
^ Clock tick
! Read bit
HiZ> M
1. HiZ
2. 1-WIRE
3. UART
4. I2C
5. SPI
6. JTAG
7. RAW2WIRE
8. RAW3WIRE
9. PC KEYBOARD
10. LCD
(1) > 4
Mode selected
Set speed:
1. ~5KHz
2. ~50KHz
3. ~100KHz
4. ~400KHz
(1) >4
READY
I2C>
Teraz je Pirát pripravený pracovať so zbernicou i2c. Zapneme napájanie a Pull-Up rezistory:
I2C> w
POWER SUPPLIES OFF
I2C> v
Voltage monitors: 5V: 0.05 | 3.3V: 0.00 | VPULLUP: 0.01 |
I2C> W
POWER SUPPLIES ON
I2C> v
Voltage monitors: 5V: 6.59 | 3.3V: 3.88 | VPULLUP: 5.00 |
I2C> P
1. Pull-ups off
2. Pull-ups on
(1) > 2
Pull-up resistors ON
I2C>
Preskenujeme zbernicu, co je na nej pripojene:
I2C> (1) <<< macro 1, I2C address search
Searching 7bit I2C address space.
Found devices at:
0xA0(0x50 W) 0xA1(0x50 R)
I2C>
Now we can talk to the chip. I needed something very simple, only to verify that the chip is OK, so I wrote random byte (I chose 0xAA) to the address 0x00 and read it back.
To write a byte to memory we need to enter this [0xA0 0x00 0xAA]
[ = Start bit 0xA0 = I2C address of the EEPROM with the WRITE bit 0x00 = Memory address 0xAA = Data ] = Stop bit
I2C> [0xA0 0x00 0xAA] I2C START BIT WRITE: 0xA0 ACK WRITE: 0x00 ACK WRITE: 0xAA ACK I2C STOP BIT I2C>
Now we need to set the read pointer to address we want to read. This is accomplished with this command [0xA0 0x00]
I2C> [0xA0 0x00] I2C START BIT WRITE: 0xA0 NACK WRITE: 0x00 NACK I2C STOP BIT I2C>
And at last we can read the byte stored at the address. [0xA1 r:1] 0xA1 = I2C address of the EEPROM with the READ bit set r:1 = tells the Bus Pirate to read 1 byte
I2C> [0xA1 rrrrr] alebo [0xA1 r:5] I2C START BIT WRITE: 0xA1 ACK READ: 0x0B ACK READ: 0xA0 ACK READ: 0x03 ACK READ: 0xAB ACK READ: 0x55 NACK I2C STOP BIT I2C>
Toto posledne sa ukazalo ze nefunguje, pretoze random read asi treba spravit takto [0xA0 0x1 0xA [0xA1 r] (opakovany start).
When you're done - na konci:
I2C> m <<<mode menu 1. HiZ ... 10. LCD (1) > <<<HiZ is the default Mode selected HiZ>
- http://www.i2c-bus.org/
- Analyzator: Bus Pirate + Logic Sniffer OLS:
- http://dangerousprototypes.com/docs/Logic_Sniffer_101
- http://dangerousprototypes.com/docs/Logic_Sniffer_102
Ukazkove programy (pre Arduino):
- Jednoduchy zapis
- Jednoduche citanie (vyzaduje aj zapis)
- Jednoduchy scan zbernice http://playground.arduino.cc/Main/I2cScanner
- Komplexny i2c scanner https://github.com/RobTillaart/Arduino/tree/master/sketches/MultiSpeedI2CScanner
K. Zbernica i2c: EEPROM
Prečítajte obsah predloženej pamäti EEPROM a zobrazte na PC.
#include <avr/interrupt.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <avr/io.h>
#include <util/delay.h>
#include <util/twi.h>
#include <stdio.h>
//#include "lcd.h"
#include "Uart_ch.h"
unsigned char RD_EEprom(unsigned char adr_RAM);
void WR_EEprom(unsigned char adr_IC,unsigned char adr_pocitadlo);
void obsluha_Stav_Aut_I2C(void);
#define ADR_IC_WR 0xA0 // EEPROM Adresa IC+WR
#define ADR_IC_RD 0xA1 // EEPROM Adresa IC+RD
volatile unsigned char buffer_I2C[10]; // buffer pre obsluhu I2C
FILE mystdout_Uart = FDEV_SETUP_STREAM(sendchar, NULL, _FDEV_SETUP_WRITE);
void WR_EEprom(unsigned char adr_IC,unsigned char adr_pocitadlo)
{ // nastavenie globalnych premennych
buffer_I2C[0]=adr_IC; // Adr obvodu + wr
buffer_I2C[1]=adr_pocitadlo; // Nastavenie Adresneho citaca 24LC04 , Adresa (z ktorej citam)/(do ktorej zapisujem)
// buffer_I2C[1]=<obsah>; // zapisovane data, byte,-ty
TWCR = _BV(TWINT) | _BV(TWSTA) | _BV(TWEN); // send start condition
// a odovzdanie riadenia "preruseniu od I2C"
obsluha_Stav_Aut_I2C();
}
unsigned char RD_EEprom(unsigned char adr_RAM)
{
// nastavenie globalnych premennych
buffer_I2C[0]=ADR_IC_RD; // Adr obvodu + rd
buffer_I2C[1]=adr_RAM; // Sem vrati obsah z nastavenej adresy 24LC04
TWCR = _BV(TWINT) | _BV(TWSTA) | _BV(TWEN); // send start condition
// a odovzdanie riadenia "preruseniu od I2C"
obsluha_Stav_Aut_I2C();
return(buffer_I2C[1]);
}
// tato funkcia vyuziva globalne premenne
// buffer_I2C[x]
// Wr_data - tato premenna nadobuda vyznam az pri komunikacii s konkretnou premennou
// vid. "instrukcny subor" I2C periferie
// implementovany instrukcny subor pre seriovu EEPROM max 256 byte
// S|adr_IO+wr|<AC>|P -- nastavenie adresneho citaca pamate EEPROM
// {nie je implementova} S|adr_IO+wr|<AC>|data|P -- zapisanie dat na nastavenu adresu pamate EEPROM
// S|adr_IO+rd|data|P -- precitanie jedneho bytu z aktualne nastavenej adresy pamate EEPROM
// obsah adresneho citaca sa inkrementne
void obsluha_Stav_Aut_I2C(void)
{ unsigned char pom_St_Aut=0;
nav:while ((TWCR & _BV(TWINT)) == 0); /* wait for transmission */
{ pom_St_Aut=TWSR & 0xf8; // precitaj stav
printf(" %02x",pom_St_Aut);
switch(pom_St_Aut)
{ case TW_START:// = 0x08 // odvysielany start
case TW_REP_START:// = 0x10 // odvysielany repeated start
TWDR = buffer_I2C[0];// Adr+wr/rd, adresa IO
TWCR = _BV(TWINT) | _BV(TWEN); /* clear interrupt to start transmission */
break;
case TW_MT_SLA_ACK: // 0x18 Data byte has been tramsmitted and ACK received
TWDR = buffer_I2C[1]; // tu konkretne, nastavenie Adreseho citaca pamate.
TWCR = _BV(TWINT) | _BV(TWEN); /* clear interrupt to start transmission */
break;
case TW_MT_DATA_ACK: // 0x28 Data byte has been tramsmitted and ACK received
TWCR = _BV(TWINT) | _BV(TWSTO) | _BV(TWEN); /* send stop condition */
return; // tento riadok v preruseni vypadne
break;
case TW_MR_SLA_ACK: // 0x40 // Data byte has been tramsmitted and NACK received
TWCR = _BV(TWINT) | _BV(TWEN) ; // clear interrupt to start transmission
break;
case TW_MR_DATA_NACK: // 0x58 // Data byte has been tramsmitted and ACK received
buffer_I2C[1]= TWDR; // Vycitaj jeden byte z 24LC04. Adresny citac sa posunie
TWCR = _BV(TWINT) | _BV(TWSTO) | _BV(TWEN); // send stop condition
return; // tento riadok v preruseni vypadne
break;
default:
TWCR = _BV(TWINT) | _BV(TWSTO) | _BV(TWEN); /* send stop condition */
return; // tento riadok v preruseni vypadne
break;
}
}
goto nav; // toto v preruseni vypadne
}
int main(void)
{ unsigned char znak;
unsigned int i=0;
unsigned char poc_adresa_EEPROM=0;
inituart(); // inicializacia UARTU // inicializacia v 4-bitovom rezime
// sei(); // Enable ALL interrupts
// ini I2C
{
TWCR = _BV(TWEN); /* send start condition */
TWBR = 72; // fi2c= fosc/(16 +2(preddelic=00=> 1)(<TWBR>)) = 100kHz
TWSR=1;
}
// TODO: to USART
/* ************************************************************ */
stdout = &mystdout_Uart;
printf("Nastavenie adresy EEPROM = %02x \n\r",poc_adresa_EEPROM);
WR_EEprom(ADR_IC_WR,poc_adresa_EEPROM);
printf("\n\r\rVypis EEPROM: \n\r");
// vypisme prvych 10 znakov
while (i<10) //256)// kapacita pamate 256 znakov, bytov,
{
znak = RD_EEprom(ADR_IC_RD); // obsah adresneho citaca EEPROM sa automaticky inkrementuje
if(znak==0xff)i=256; // vymazane pametove miesto
{
printf(" %02d %02x %c\r",i++,znak,znak);
}
}
for(;;); // a cakam napr. na "RESET"
}