Tester obvodu 7400: Rozdiel medzi revíziami
Zo stránky SensorWiki
Bez shrnutí editace |
Bez shrnutí editace |
||
| Riadok 34: | Riadok 34: | ||
<tabs> | <tabs> | ||
<tab name="AVR C-code"><source lang="c++" style="background: LightYellow;"> | <tab name="AVR C-code"><source lang="c++" style="background: LightYellow;"> | ||
#include <avr/io.h> | #include <avr/io.h> | ||
#include <util/delay.h> | #include <util/delay.h> | ||
#include <stdio.h> | #include <stdio.h> | ||
#include "uart.h" | #include "uart.h" | ||
FILE mystdout = FDEV_SETUP_STREAM(uart_putc, NULL, _FDEV_SETUP_WRITE); | FILE mystdout = FDEV_SETUP_STREAM(uart_putc, NULL, _FDEV_SETUP_WRITE); | ||
#define F_CPU 16000000UL | #define F_CPU 16000000UL | ||
#define BAUD 9600 | #define BAUD 9600 | ||
#define NAND_A_PIN PD6 | #define NAND_A_PIN PD6 | ||
#define NAND_B_PIN PD7 | #define NAND_B_PIN PD7 | ||
#define NAND_OUT_PIN PB0 | #define NAND_OUT_PIN PB0 | ||
#define NAND_C_PIN PD5 | |||
#define NAND_D_PIN PD4 | |||
#define NAND_OUT2_PIN PD3 | |||
#define NAND_E_PIN PC0 | |||
#define NAND_F_PIN PC1 | |||
#define NAND_OUT3_PIN PC2 | |||
#define NAND_G_PIN PB3 | |||
#define NAND_H_PIN PB4 | |||
#define NAND_OUT4_PIN PB5 | |||
// This part includes necessary libraries and defines macros and pins. | |||
// Sets communication via UART. | |||
void init_pins() { | void init_pins() { | ||
DDRD |= (1 << NAND_A_PIN) | (1 << NAND_B_PIN); | DDRD |= (1 << NAND_A_PIN) | (1 << NAND_B_PIN) | (1 << NAND_C_PIN) | (1 << NAND_D_PIN); | ||
DDRB &= ~(1 << NAND_OUT_PIN); | DDRB |= (1 << NAND_G_PIN) | (1 << NAND_H_PIN); | ||
DDRC |= (1 << NAND_E_PIN) | (1 << NAND_F_PIN); | |||
DDRB &= ~(1 << NAND_OUT_PIN); | |||
DDRD &= ~(1 << NAND_OUT2_PIN); | |||
DDRC &= ~(1 << NAND_OUT3_PIN); | |||
DDRB &= ~(1 << NAND_OUT4_PIN); | |||
} | } | ||
void send_input_signals(uint8_t a, uint8_t b) { | void send_input_signals(uint8_t a, uint8_t b, uint8_t c, uint8_t d, uint8_t e, uint8_t f, uint8_t g, uint8_t h) { | ||
if (a) PORTD |= (1 << NAND_A_PIN); | if (a) PORTD |= (1 << NAND_A_PIN); | ||
else PORTD &= ~(1 << NAND_A_PIN); | else PORTD &= ~(1 << NAND_A_PIN); | ||
if (b) PORTD |= (1 << NAND_B_PIN); | if (b) PORTD |= (1 << NAND_B_PIN); | ||
else PORTD &= ~(1 << NAND_B_PIN); | else PORTD &= ~(1 << NAND_B_PIN); | ||
if (c) PORTD |= (1 << NAND_C_PIN); | |||
else PORTD &= ~(1 << NAND_C_PIN); | |||
if (d) PORTD |= (1 << NAND_D_PIN); | |||
else PORTD &= ~(1 << NAND_D_PIN); | |||
if (e) PORTC |= (1 << NAND_E_PIN); | |||
else PORTC &= ~(1 << NAND_E_PIN); | |||
if (f) PORTC |= (1 << NAND_F_PIN); | |||
else PORTC &= ~(1 << NAND_F_PIN); | |||
if (g) PORTB |= (1 << NAND_G_PIN); | |||
else PORTB &= ~(1 << NAND_G_PIN); | |||
if (h) PORTB |= (1 << NAND_H_PIN); | |||
else PORTB &= ~(1 << NAND_H_PIN); | |||
} | |||
uint8_t read_output_signal(uint8_t pin, uint8_t port) { | |||
switch (port) { | |||
case 'B': | |||
return (PINB & (1 << pin)) != 0; | |||
case 'D': | |||
return (PIND & (1 << pin)) != 0; | |||
case 'C': | |||
return (PINC & (1 << pin)) != 0; | |||
default: | |||
return 0; | |||
} | |||
} | |||
int main() { | int main() { | ||
| Riadok 76: | Riadok 116: | ||
for (;;) { | for (;;) { | ||
send_input_signals(1, 0); | send_input_signals(1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0); | ||
printf("Vystup pro 10: %d\r\n", | int output = read_output_signal(NAND_OUT_PIN, 'B'); | ||
_delay_ms(1000); | printf("Vystup pro 10: %d\r\n", output); | ||
if (output == 1) { | |||
printf("OK\n"); | |||
} else { | |||
printf("Nie je OK\n"); | |||
} | |||
_delay_ms(1000); | |||
send_input_signals(1, 1); | send_input_signals(1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0); | ||
printf("Vystup pro 11: %d\r\n", | int output2 = read_output_signal(NAND_OUT2_PIN, 'D'); | ||
_delay_ms(1000); | printf("Vystup pro 11: %d\r\n", output2); | ||
if (output2 == 1) { | |||
printf("Nie je OK\n"); | |||
} else { | |||
printf("OK\n"); | |||
} | |||
_delay_ms(1000); | |||
send_input_signals(0, 1); | send_input_signals(0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0); | ||
printf("Vystup pro 01: %d\r\n", | int output3 = read_output_signal(NAND_OUT3_PIN, 'C'); | ||
_delay_ms(1000); | printf("Vystup pro 01: %d\r\n", output3); | ||
if (output3 == 1) { | |||
printf("OK\n"); | |||
} else { | |||
printf("Nie je OK\n"); | |||
} | |||
_delay_ms(1000); | |||
send_input_signals(0, 0); | send_input_signals(0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0); | ||
printf("Vystup pro 00: %d\r\n", | int output4 = read_output_signal(NAND_OUT4_PIN, 'B'); | ||
_delay_ms(1000); | printf("Vystup pro 00: %d\r\n", output4); | ||
if (output4 == 1) { | |||
printf("OK\n"); | |||
} else { | |||
printf("Nie je OK\n"); | |||
} | |||
_delay_ms(1000); | |||
} | } | ||
return 0; | return 0; | ||
} | } | ||
</source></tab> | </source></tab> | ||
Verzia z 17:23, 22. máj 2024
Záverečný projekt predmetu MIPS / LS2024 - Jakub Macák
Zadanie
Mojou úlohou bolo spraviť tester obvodu 7400 (4xNAND), pripojeného k doske Arduino UNO
Literatúra:
Analýza a opis riešenia
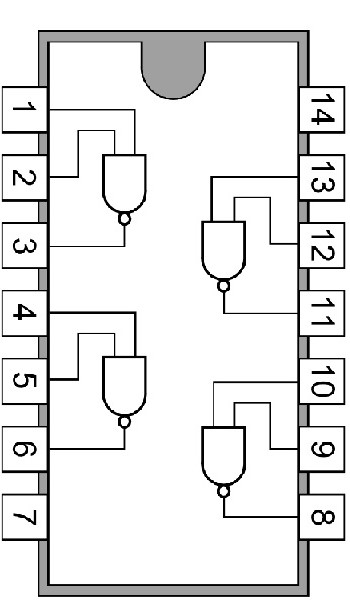
Obvod 7400 (4xNAND) je obvod, ktorý obsahuje štyri samostatné NAND brány, pričom každá brána má dva vstupy a jeden výstup. Najskôr som si musel zistiť PIN layout tohto obvodu a následne obvod správne zapojiť. Po zapojení som spravil program, ktorý posiela do obvodu kombinácie (1) jednotiek a (0) núl. Obvod kombinácie vyhodnotí a odošle hodnotu na základe danej kombinácie. Keďže to je NAND obvod, v prípade kombinácie 1-1 vracia 0, pre každú inú kombináciu vracia 1.
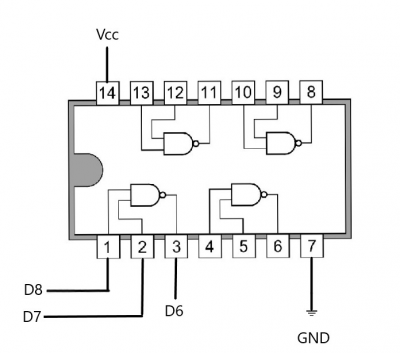
Zapojenie
Zapojenie som realizoval zapojením pinu 1 na D8, 2 na D7 a 3 na D6. Pin 7 na GND a 14 na Vcc.
Algoritmus a program
Algoritmus programu je....
#include <avr/io.h>
#include <util/delay.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "uart.h"
FILE mystdout = FDEV_SETUP_STREAM(uart_putc, NULL, _FDEV_SETUP_WRITE);
#define F_CPU 16000000UL
#define BAUD 9600
#define NAND_A_PIN PD6
#define NAND_B_PIN PD7
#define NAND_OUT_PIN PB0
#define NAND_C_PIN PD5
#define NAND_D_PIN PD4
#define NAND_OUT2_PIN PD3
#define NAND_E_PIN PC0
#define NAND_F_PIN PC1
#define NAND_OUT3_PIN PC2
#define NAND_G_PIN PB3
#define NAND_H_PIN PB4
#define NAND_OUT4_PIN PB5
// This part includes necessary libraries and defines macros and pins.
// Sets communication via UART.
void init_pins() {
DDRD |= (1 << NAND_A_PIN) | (1 << NAND_B_PIN) | (1 << NAND_C_PIN) | (1 << NAND_D_PIN);
DDRB |= (1 << NAND_G_PIN) | (1 << NAND_H_PIN);
DDRC |= (1 << NAND_E_PIN) | (1 << NAND_F_PIN);
DDRB &= ~(1 << NAND_OUT_PIN);
DDRD &= ~(1 << NAND_OUT2_PIN);
DDRC &= ~(1 << NAND_OUT3_PIN);
DDRB &= ~(1 << NAND_OUT4_PIN);
}
void send_input_signals(uint8_t a, uint8_t b, uint8_t c, uint8_t d, uint8_t e, uint8_t f, uint8_t g, uint8_t h) {
if (a) PORTD |= (1 << NAND_A_PIN);
else PORTD &= ~(1 << NAND_A_PIN);
if (b) PORTD |= (1 << NAND_B_PIN);
else PORTD &= ~(1 << NAND_B_PIN);
if (c) PORTD |= (1 << NAND_C_PIN);
else PORTD &= ~(1 << NAND_C_PIN);
if (d) PORTD |= (1 << NAND_D_PIN);
else PORTD &= ~(1 << NAND_D_PIN);
if (e) PORTC |= (1 << NAND_E_PIN);
else PORTC &= ~(1 << NAND_E_PIN);
if (f) PORTC |= (1 << NAND_F_PIN);
else PORTC &= ~(1 << NAND_F_PIN);
if (g) PORTB |= (1 << NAND_G_PIN);
else PORTB &= ~(1 << NAND_G_PIN);
if (h) PORTB |= (1 << NAND_H_PIN);
else PORTB &= ~(1 << NAND_H_PIN);
}
uint8_t read_output_signal(uint8_t pin, uint8_t port) {
switch (port) {
case 'B':
return (PINB & (1 << pin)) != 0;
case 'D':
return (PIND & (1 << pin)) != 0;
case 'C':
return (PINC & (1 << pin)) != 0;
default:
return 0;
}
}
int main() {
init_pins();
uart_init();
stdout = &mystdout;
printf("Kombinacie:\n");
for (;;) {
send_input_signals(1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0);
int output = read_output_signal(NAND_OUT_PIN, 'B');
printf("Vystup pro 10: %d\r\n", output);
if (output == 1) {
printf("OK\n");
} else {
printf("Nie je OK\n");
}
_delay_ms(1000);
send_input_signals(1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0);
int output2 = read_output_signal(NAND_OUT2_PIN, 'D');
printf("Vystup pro 11: %d\r\n", output2);
if (output2 == 1) {
printf("Nie je OK\n");
} else {
printf("OK\n");
}
_delay_ms(1000);
send_input_signals(0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0);
int output3 = read_output_signal(NAND_OUT3_PIN, 'C');
printf("Vystup pro 01: %d\r\n", output3);
if (output3 == 1) {
printf("OK\n");
} else {
printf("Nie je OK\n");
}
_delay_ms(1000);
send_input_signals(0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0);
int output4 = read_output_signal(NAND_OUT4_PIN, 'B');
printf("Vystup pro 00: %d\r\n", output4);
if (output4 == 1) {
printf("OK\n");
} else {
printf("Nie je OK\n");
}
_delay_ms(1000);
}
return 0;
}
/* ************************************************************************* */
/* FileName: uart.h */
/* ************************************************************************* */
#define LED PB5 // internal on-board LED
/* na testovanie su uz zadefinovane */
// bit_is_set(PINB, SW1)
// bit_is_clear(PINB, SW1)
/* na cakanie su preddefinovane slucky */
// loop_until_bit_is_set(PINB, SW1); // cakanie na uvolnenie tlacitka
// loop_until_bit_is_clear(PINB, SW1); // cakanie na stlacenie tlacitka
#define set_bit(ADDRESS,BIT) (ADDRESS |= (1<<BIT))
#define clear_bit(ADDRESS,BIT) (ADDRESS &= ~(1<<BIT))
#ifndef UART_H_
#define UART_H_
#include <stdio.h>
#define BAUD_PRESCALE (((F_CPU / (BAUDRATE * 16UL))) - 1) // vzor?ek z datasheetu
void hw_init( void );
void uart_init( void );
/* Following definition is compatible with STDIO.H, for more
* information see https://www.appelsiini.net/2011/simple-usart-with-avr-libc/
*/
int uart_putc( char c, FILE *stream );
void uart_puts( const char *s );
char uart_getc( void );
void delay(int delay);
#endif /* UART_H_ */
/* ************************************************************************* */
/* FileName: uart.c */
/* ************************************************************************* */
#include <avr/io.h>
#include <util/delay.h>
#include "uart.h"
void hw_init( void )
{
DDRB |= (1<<LED); // PORTB.5 kde je LED ma byt OUTPUT
/* sem si mozete dopisat svoje vlastne inicializacne prikazy */
}
void uart_init( void )
{
// for different BAUD rate change the project settings, or uncomment
// following two lines:
// #undef BAUD // avoid compiler warning
// #define BAUD 115200
#include <util/setbaud.h> // requires defined BAUD
UBRR0H = UBRRH_VALUE;
UBRR0L = UBRRL_VALUE;
#if USE_2X // defined in setbaud.h
UCSR0A |= (1 << U2X0);
#else
UCSR0A &= ~(1 << U2X0);
#endif
UCSR0C = _BV(UCSZ01) | _BV(UCSZ00); /* 8-bit data */
UCSR0B = _BV(RXEN0) | _BV(TXEN0); /* Enable RX and TX */
}
int uart_putc( char c, FILE *stream )
{
if (c == '\n')
uart_putc('\r',stream);
loop_until_bit_is_set(UCSR0A, UDRE0); /* Wait until data register empty. */
UDR0 = c;
return 0;
}
void uart_puts(const char *s)
{
/* toto je vasa uloha */
}
char uart_getc(void)
{
loop_until_bit_is_set(UCSR0A, RXC0); /* Wait until data exists. */
return UDR0;
}
void delay(int delay) // vlastna funkcia pre dlhsie casy
{
for (int i=1; i<=delay; i++)
_delay_ms(1);
}
//V tejto časti sa inicializujú piny, UART komunikácia, a je nastavený výstup pre stdout pre použitie funkcie printf(). Následne sa v nekonečnej slučke posielajú rôzne kombinácie vstupných signálov pomocou send_input_signals() a číta sa a vypisuje výstupný signál pomocou printf() a read_output_signal() do Serialu. </source></tab> </tabs>
Zdrojový kód: Macáksemestralna.zip
Overenie
Na overenie toho, či naozaj tento obvod funguje správne, použijeme Serial na vypisovanie kombinácií jednotiek a núl, a hodnôt, ktoré obvod vracia.

Video: