MEMS cvičenie 2: Rozdiel medzi revíziami
Zo stránky SensorWiki
Bez shrnutí editace |
Bez shrnutí editace |
||
| Riadok 49: | Riadok 49: | ||
} | } | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
== Pripojenie LED a LCD displeja a lokálne zobrazenie meranej veličiny == | |||
V tejto časti cvičenia zobrazíme meranú veličinu na miestnom LCD displeji mikropočítača. | |||
== Programovateľný LCD displej == | |||
* LCD zobrazovač. Klávesnica. <BR>[http://ap.urpi.fei.stuba.sk/mmp/prednaska02.pdf Obšírnejšie informácie o displejoch] (prednáška z predmetu MMP) | |||
=== LCD Modul === | |||
[[Obrázok:ParallaxLCDAppMod.jpg|left]] | |||
'''Vlastnosti:''' | |||
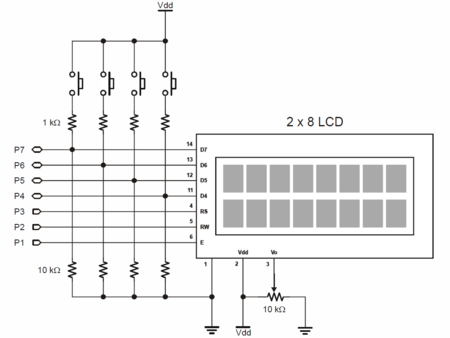
* 2x8 LCD Displej bez podsvetlenia | |||
* 4 Tlačítka | |||
* Trimer na zmenu kontrastu | |||
'''Technické parametre:''' | |||
* Napájanie: 5 V @ 15 mA | |||
* Pripojenie: 4-Bit parallel interface (Hitachi HD44780 compatible) | |||
* Rozmery: 60 x 50 x 20 mm | |||
* Pracovná teplota: 0 až +70 °C | |||
[[Obrázok:Acrob_LCD_Schematic.png|center]] | |||
[[Obrázok:Acrob_LCD_Schema2.png|800px|center]] | |||
Najprv sa snažte pochopiť, ako je vytvorený vzorový program, ako sa konfiguruje pripojenie LCD k portom, skontrolujte konfiguráciu. Potom modifikujte program z predošlého cvičenia tak, aby | |||
sa meraná hodnota polohy potenciometra zobrazila na displeji. Zobrazte aj inžinierske jednotky. | |||
=== Literatúra === | |||
* Katalógové listy | |||
** Radič Hitachi [http://ap.urpi.fei.stuba.sk/mmp/HD44780.pdf HD44780] | |||
** Displej 2x16 [http://ap.urpi.fei.stuba.sk/mmp/DEM16216SYH-LY.pdf DEM 16216 SYH-LY] | |||
** Displej 2x16 [http://ap.urpi.fei.stuba.sk/mmp/DEM20231SYH-PY.pdf DEM 20231 SYH-PY] | |||
** 2x16 Parallel LCD [http://www.parallax.com/Portals/0/Downloads/docs/prod/audiovis/lcd2x16par.pdf datasheet] | |||
** Podrobné manuály sú aj u [http://www.hantronix.com/page/index/products/character výrobcu Hantronix]. | |||
* Peter Ouwehand: '''[http://home.iae.nl/users/pouweha/lcd/lcd.shtml How to control a HD44780-based Character-LCD]''' | |||
* Ian Harries: ''[http://www.doc.ic.ac.uk/%7Eih/doc/lcd/ HD44780-Based LCD Modules]''' | |||
* Tomáš Dresler: '''[http://www.hw.cz/ART632-Inteligentni-displeje-a-jejich-pripojeni-k-PC.html Inteligentní displeje a jejich připojení k PC]'''. [hw.cz] | |||
* Nuts & Volts: [http://www.parallax.com/dl/docs/cols/nv/vol1/col/nv31.pdf Demystifying Character Based LCDs] | |||
* Stamp Works - pp. 73 and more [http://www.parallax.com/Portals/0/Downloads/docs/books/sw/Web-SW-v2.1.pdf] | |||
=== Arduino === | |||
Nasledovný príklad je pre Arduino. | |||
Pozn.: Ak budete vypisovať najprv štvorciferné číslo a potom trojciferné, nezabudnite to štvorciferné najprv vymazať, inak vám tam posledná cifra bude "visieť". Vymazať sa dá napríklad takto: | |||
// 12345678 | |||
lcd.print(" "); | |||
* [https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/LiquidCrystal LCD Library] | |||
<source lang="c"> | |||
/* | |||
LiquidCrystal Library - Hello World | |||
Demonstrates the use a 8x2 LCD display. | |||
The circuit: | |||
* LCD RS pin to digital pin 3 | |||
* LCD R/W pin to digital pin 2 | |||
* LCD Enable pin to digital pin 1 | |||
* LCD D4 pin to digital pin 4 | |||
* LCD D5 pin to digital pin 5 | |||
* LCD D6 pin to digital pin 6 | |||
* LCD D7 pin to digital pin 7 | |||
*/ | |||
#include <LiquidCrystal.h> // include the library | |||
// initialize the library with the numbers of the interface pins | |||
// LiquidCrystal(RS, RW, EN, D4, D5, D6, D7) | |||
LiquidCrystal lcd( 3, 2, 1, 4, 5, 6, 7); | |||
void setup() { | |||
// set up the LCD's number of columns and rows: | |||
lcd.begin(8, 2); | |||
// Print a message to the LCD. | |||
lcd.print("Ahoj!"); | |||
} | |||
void loop() { | |||
// set the cursor to column 0, line 1 | |||
// (note: line 1 is the second row, since counting begins with 0): | |||
lcd.setCursor(0, 1); | |||
// print the number of seconds since reset: | |||
lcd.print(millis()/1000); | |||
// print the status of buttons: | |||
lcd.setCursor(6, 0); | |||
lcd.print(ReadButtons(),HEX); | |||
} | |||
/* ------------------------------------------------------- */ | |||
/* Read and debounce the LCD AppMod buttons */ | |||
/* */ | |||
/* Returns 0 if nothing is pressed */ | |||
/* Returns 1 if button A is pressed */ | |||
/* Returns 2 if button B is pressed */ | |||
/* Returns 4 if button C is pressed */ | |||
/* Returns 8 if button D is pressed */ | |||
/* Returns combination if more is pressed (e.g. 6 for B+C)*/ | |||
/* */ | |||
/* ------------------------------------------------------- */ | |||
unsigned char ReadButtons() | |||
{ | |||
DDRD = 0b00001110; // make LCD bus inputs | |||
unsigned char state = 0xFF; // assume nothing pressed | |||
for(int scan = 1; scan<=10; scan++) | |||
{ | |||
state = state & ((PIND&0xF0)>>4); // make sure button held | |||
delay(5); // debounce 10 x 5 ms | |||
} | |||
DDRD = 0b11111110; // return bus to outputs | |||
return(state); | |||
} | |||
</source> | |||
Misc: | |||
* [http://www.geocities.com/dinceraydin/djlcdsim/djlcdsim.html LCD Display Simulator] | |||
* [http://www.geocities.com/dinceraydin/lcd/charcalc.htm Custom Character Calculator] | |||
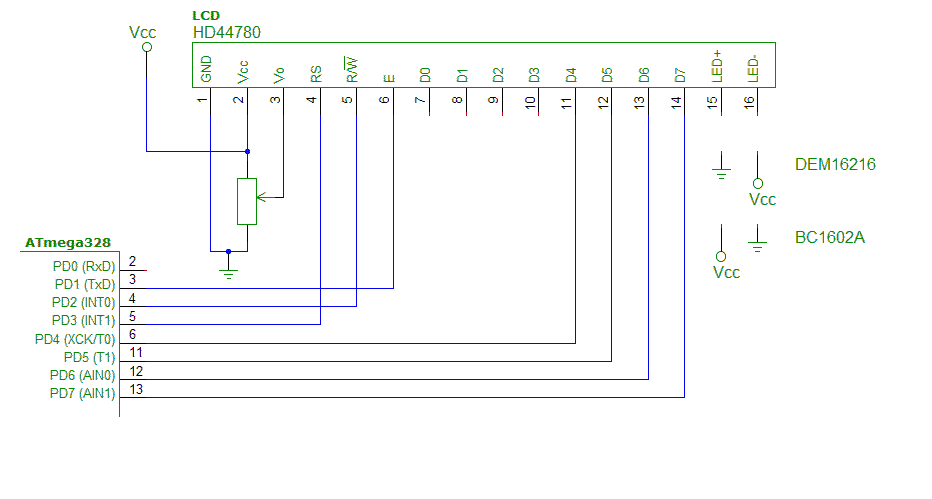
Prečo je takto napísaná a ako vlastne funguje lepšie zistíte, keď si preštudujete schému zapojenia: | |||
[[Obrázok:LCD_App_Mod_Schematic.png|center|450px]] | |||
== Sedemsegmentový 4-miestny LED displej == | |||
* 4-miestny 7-segmentový displej | |||
** Product page http://www.gme.sk/hd-m324rd-p512-924 | |||
** Datasheet http://www.gme.sk/img/cache/doc/512/924/hd-m324rd-datasheet-1.pdf | |||
** Animácia k 7seg displeju: http://www.uize.com/examples/seven-segment-display.html | |||
=== Programovanie === | |||
Z tejto časti nemusíte mať obavy, programovanie je jednoduché a budeme využívať existujúce | |||
programy s knižnicami, ktoré si len zľahka modifikujete pre svoje potreby. | |||
* Programovací jazyk aj prostredie: [https://www.arduino.cc/ Arduino] | |||
* Knižnica SevSeg: https://github.com/sparkfun/SevSeg | |||
Ukážkové programy: | |||
<source lang=c> | |||
#include <SevSeg.h> | |||
SevSeg MyDisp; //Instantiate a seven segment controller object | |||
void setup() | |||
{ | |||
byte numDigits = 4; | |||
byte digitPins[] = {2, 3, 4, 5}; // Digits: 1,2,3,4 | |||
byte segmentPins[] = {6, 7, 8, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15}; // Segments: A,B,C,D,E,F,G,Period | |||
MyDisp.begin(COMMON_ANODE, numDigits, digitPins, segmentPins); | |||
MyDisp.setBrightness(80); | |||
} | |||
void loop() | |||
{ | |||
MyDisp.setNumber(1234,9); // Second argument is decimal place | |||
MyDisp.refreshDisplay(); // Must run repeatedly | |||
} | |||
</source> | |||
<source lang="c"> | |||
#include "SevSeg.h" | |||
SevSeg myDisplay; | |||
#define FOUR_DIGITS 4 | |||
#define A1 2 | |||
#define A2 3 | |||
#define A3 4 | |||
#define A4 5 | |||
#define SegA 6 | |||
#define SegB 7 | |||
#define SegC 8 | |||
int value; | |||
int oldvalue; | |||
char tempString[5]; | |||
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
void setup() | |||
{ | |||
value = 0; | |||
oldvalue = 0; | |||
myDisplay.Begin(COMMON_ANODE, FOUR_DIGITS, A1, A2, A3, A4, SegA, SegB, SegC, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15); | |||
myDisplay.SetBrightness(100); //Set the display to 100% brightness level | |||
} | |||
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
void loop() | |||
{ | |||
value = analogRead(5); // measurement | |||
value = (15*oldvalue + value)/16; // simple filter | |||
sprintf(tempString, "%4d", (long)value, DEC); // create output string | |||
myDisplay.DisplayString(tempString, 0); // display value on disp | |||
oldvalue = value; | |||
} | |||
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | |||
</source> | |||
Rozličné neusporiadané linky: | |||
* Animácia k 7seg displeju: http://www.uize.com/examples/seven-segment-display.html | |||
* Nas displej: | |||
** Product page http://www.gme.sk/hd-m324rd-p512-924 | |||
** Datasheet http://www.gme.sk/img/cache/doc/512/924/hd-m324rd-datasheet-1.pdf | |||
* Schema zapojenia Arduino https://www.arduino.cc/en/uploads/Main/Arduino-Pro-schematic.pdf | |||
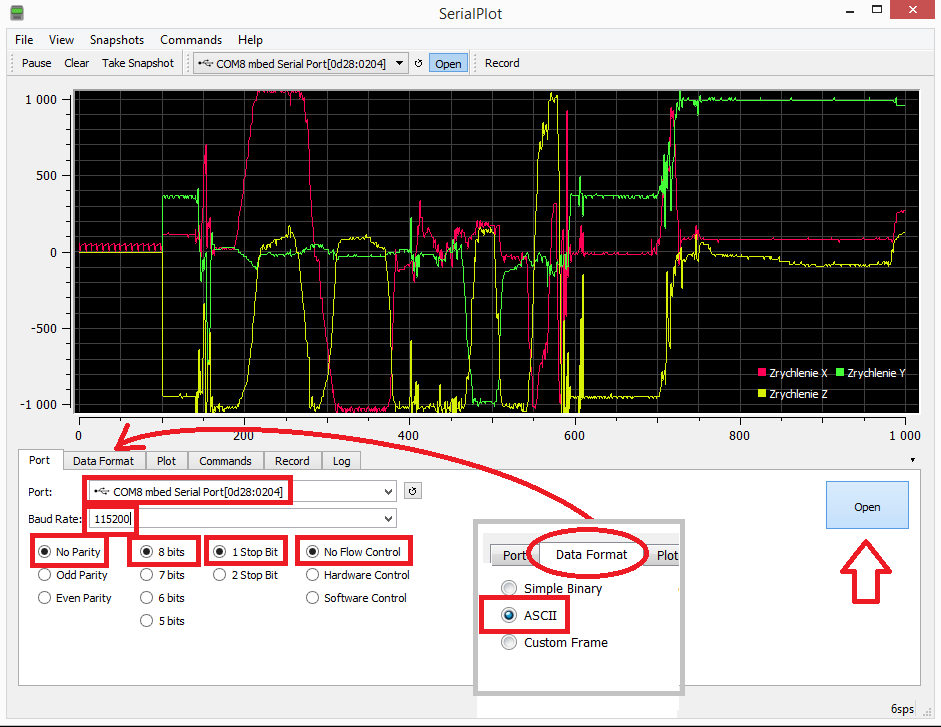
== Grafické priebehy na PC --Serial Plotter === | |||
[[Súbor:IconSerialPlotter.png|left]] Serial Plotter je trocha sofistikovanejší program ako Terminal, jeho úlohou je zakresliť graficky všetky prijaté informácie. Najjednoduchšie je posielať mu čísla, pričom ich môže byť aj viac, oddelených čiarkami. Každá jedna n-tica hodnôt musí končíť znakom pre nový riadok. V knižnici Serial použite bloky Serial Write Number pre čísla, Serial Write String pre čiarky a Serial Write Line pre ukončenie riadka. Neposielajte hodnoty príliš často, aby sa nepreplnil vstupný buffer. | |||
* [https://hackaday.io/project/5334-serialplot-realtime-plotting-software Domovská stránka programu] | |||
* [http://senzor.robotika.sk/zp/serialplot.zip Lokálna kópia] | |||
<BR><BR> | |||
[[Súbor:SerialPlotter01.png]] | |||
<BR> | |||
<BR> | |||
* Graphics in Arduino IDE: http://www.idogendel.com/en/archives/489 | |||
* https://rheingoldheavy.com/new-arduino-serial-plotter/ | |||
Trocha zlozitejsie: | |||
* http://arduino.stackexchange.com/questions/1180/serial-data-plotting-programs | |||
* https://github.com/nprasan/ardugraph | |||
[[MEMS inteligentné senzory a aktuátory#Cvi.C4.8Denia|Návrat na zoznam cvičení...]] | |||
[[Category:MEMS]] | |||
== Linearizácia prevodovej charakteristiky == | == Linearizácia prevodovej charakteristiky == | ||
| Riadok 98: | Riadok 371: | ||
* https://www.gnu.org/software/gsl/manual/html_node/Example-programs-for-Nonlinear-Least_002dSquares-Fitting.html | * https://www.gnu.org/software/gsl/manual/html_node/Example-programs-for-Nonlinear-Least_002dSquares-Fitting.html | ||
* https://www.gnu.org/software/octave/doc/interpreter/One_002ddimensional-Interpolation.html#One_002ddimensional-Interpolation | * https://www.gnu.org/software/octave/doc/interpreter/One_002ddimensional-Interpolation.html#One_002ddimensional-Interpolation | ||
== Úlohy == | == Úlohy == | ||
Verzia z 13:26, 2. marec 2020
Poznamky 2020: https://www.qsl.net/om3cph/sw/pot.html https://electronics.stackexchange.com/questions/231522/improving-the-linearity-of-a-potentiometer-after-loading http://www.geofex.com/article_folders/potsecrets/potscret.htm
Potenciometrické snímače
- Poskladajte si odporový senzor polohy so stupnicou.
- Zmerajte prevodovú charakteristiku odporového senzora polohy pomocou ohmmetra.
- Senzor pripojte k A/D prevodníku mikropočítača a pomocou programu nižšie zmerajte prevodovú charakteristiku celého meracieho člena.
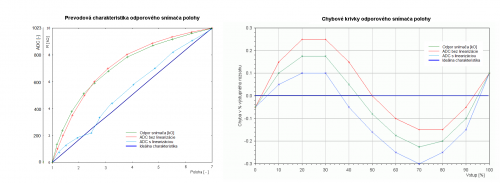
- Prevodovú charakteristiku zlinearizujte a doložte úspešnosť porovnaním metrologických parametrov.
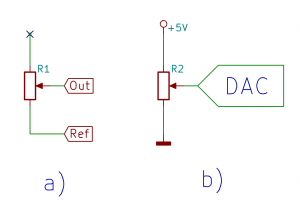
- Príklad na pripojenie analógového senzora: http://senzor.robotika.sk/sensorwiki/index.php/Acrob007
- Riadiaca doska Acrob http://senzor.robotika.sk/sensorwiki/index.php/Acrob
- Technická dokumentácia http://senzor.robotika.sk/sensorwiki/index.php/Acrob_technical_description
- Arduino homepage https://www.arduino.cc/
#define positionSensor 5 // define your pin here
int adcValue;
float outputValue;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); // typical values are 9600 or 115200
}
void loop()
{
adcValue = analogRead(positionSensor); // read ADC value
/* ======= replace this section with your code ===== */
outputValue = adcValue;
/* ================================================== */
Serial.println( outputValue ); // prints value over serial
delay(100); // delay in milliseconds
}
Pripojenie LED a LCD displeja a lokálne zobrazenie meranej veličiny
V tejto časti cvičenia zobrazíme meranú veličinu na miestnom LCD displeji mikropočítača.
Programovateľný LCD displej
- LCD zobrazovač. Klávesnica.
Obšírnejšie informácie o displejoch (prednáška z predmetu MMP)
LCD Modul

Vlastnosti:
- 2x8 LCD Displej bez podsvetlenia
- 4 Tlačítka
- Trimer na zmenu kontrastu
Technické parametre:
- Napájanie: 5 V @ 15 mA
- Pripojenie: 4-Bit parallel interface (Hitachi HD44780 compatible)
- Rozmery: 60 x 50 x 20 mm
- Pracovná teplota: 0 až +70 °C
Najprv sa snažte pochopiť, ako je vytvorený vzorový program, ako sa konfiguruje pripojenie LCD k portom, skontrolujte konfiguráciu. Potom modifikujte program z predošlého cvičenia tak, aby
sa meraná hodnota polohy potenciometra zobrazila na displeji. Zobrazte aj inžinierske jednotky.
Literatúra
- Katalógové listy
- Radič Hitachi HD44780
- Displej 2x16 DEM 16216 SYH-LY
- Displej 2x16 DEM 20231 SYH-PY
- 2x16 Parallel LCD datasheet
- Podrobné manuály sú aj u výrobcu Hantronix.
- Peter Ouwehand: How to control a HD44780-based Character-LCD
- Ian Harries: HD44780-Based LCD Modules'
- Tomáš Dresler: Inteligentní displeje a jejich připojení k PC. [hw.cz]
- Nuts & Volts: Demystifying Character Based LCDs
- Stamp Works - pp. 73 and more [1]
Arduino
Nasledovný príklad je pre Arduino.
Pozn.: Ak budete vypisovať najprv štvorciferné číslo a potom trojciferné, nezabudnite to štvorciferné najprv vymazať, inak vám tam posledná cifra bude "visieť". Vymazať sa dá napríklad takto:
// 12345678
lcd.print(" ");
/*
LiquidCrystal Library - Hello World
Demonstrates the use a 8x2 LCD display.
The circuit:
* LCD RS pin to digital pin 3
* LCD R/W pin to digital pin 2
* LCD Enable pin to digital pin 1
* LCD D4 pin to digital pin 4
* LCD D5 pin to digital pin 5
* LCD D6 pin to digital pin 6
* LCD D7 pin to digital pin 7
*/
#include <LiquidCrystal.h> // include the library
// initialize the library with the numbers of the interface pins
// LiquidCrystal(RS, RW, EN, D4, D5, D6, D7)
LiquidCrystal lcd( 3, 2, 1, 4, 5, 6, 7);
void setup() {
// set up the LCD's number of columns and rows:
lcd.begin(8, 2);
// Print a message to the LCD.
lcd.print("Ahoj!");
}
void loop() {
// set the cursor to column 0, line 1
// (note: line 1 is the second row, since counting begins with 0):
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
// print the number of seconds since reset:
lcd.print(millis()/1000);
// print the status of buttons:
lcd.setCursor(6, 0);
lcd.print(ReadButtons(),HEX);
}
/* ------------------------------------------------------- */
/* Read and debounce the LCD AppMod buttons */
/* */
/* Returns 0 if nothing is pressed */
/* Returns 1 if button A is pressed */
/* Returns 2 if button B is pressed */
/* Returns 4 if button C is pressed */
/* Returns 8 if button D is pressed */
/* Returns combination if more is pressed (e.g. 6 for B+C)*/
/* */
/* ------------------------------------------------------- */
unsigned char ReadButtons()
{
DDRD = 0b00001110; // make LCD bus inputs
unsigned char state = 0xFF; // assume nothing pressed
for(int scan = 1; scan<=10; scan++)
{
state = state & ((PIND&0xF0)>>4); // make sure button held
delay(5); // debounce 10 x 5 ms
}
DDRD = 0b11111110; // return bus to outputs
return(state);
}
Misc:
Prečo je takto napísaná a ako vlastne funguje lepšie zistíte, keď si preštudujete schému zapojenia:
Sedemsegmentový 4-miestny LED displej
- 4-miestny 7-segmentový displej
- Product page http://www.gme.sk/hd-m324rd-p512-924
- Datasheet http://www.gme.sk/img/cache/doc/512/924/hd-m324rd-datasheet-1.pdf
- Animácia k 7seg displeju: http://www.uize.com/examples/seven-segment-display.html
Programovanie
Z tejto časti nemusíte mať obavy, programovanie je jednoduché a budeme využívať existujúce programy s knižnicami, ktoré si len zľahka modifikujete pre svoje potreby.
- Programovací jazyk aj prostredie: Arduino
- Knižnica SevSeg: https://github.com/sparkfun/SevSeg
Ukážkové programy:
#include <SevSeg.h>
SevSeg MyDisp; //Instantiate a seven segment controller object
void setup()
{
byte numDigits = 4;
byte digitPins[] = {2, 3, 4, 5}; // Digits: 1,2,3,4
byte segmentPins[] = {6, 7, 8, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15}; // Segments: A,B,C,D,E,F,G,Period
MyDisp.begin(COMMON_ANODE, numDigits, digitPins, segmentPins);
MyDisp.setBrightness(80);
}
void loop()
{
MyDisp.setNumber(1234,9); // Second argument is decimal place
MyDisp.refreshDisplay(); // Must run repeatedly
}
#include "SevSeg.h"
SevSeg myDisplay;
#define FOUR_DIGITS 4
#define A1 2
#define A2 3
#define A3 4
#define A4 5
#define SegA 6
#define SegB 7
#define SegC 8
int value;
int oldvalue;
char tempString[5];
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setup()
{
value = 0;
oldvalue = 0;
myDisplay.Begin(COMMON_ANODE, FOUR_DIGITS, A1, A2, A3, A4, SegA, SegB, SegC, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15);
myDisplay.SetBrightness(100); //Set the display to 100% brightness level
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void loop()
{
value = analogRead(5); // measurement
value = (15*oldvalue + value)/16; // simple filter
sprintf(tempString, "%4d", (long)value, DEC); // create output string
myDisplay.DisplayString(tempString, 0); // display value on disp
oldvalue = value;
}
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Rozličné neusporiadané linky:
- Animácia k 7seg displeju: http://www.uize.com/examples/seven-segment-display.html
- Nas displej:
- Schema zapojenia Arduino https://www.arduino.cc/en/uploads/Main/Arduino-Pro-schematic.pdf
Grafické priebehy na PC --Serial Plotter =

Serial Plotter je trocha sofistikovanejší program ako Terminal, jeho úlohou je zakresliť graficky všetky prijaté informácie. Najjednoduchšie je posielať mu čísla, pričom ich môže byť aj viac, oddelených čiarkami. Každá jedna n-tica hodnôt musí končíť znakom pre nový riadok. V knižnici Serial použite bloky Serial Write Number pre čísla, Serial Write String pre čiarky a Serial Write Line pre ukončenie riadka. Neposielajte hodnoty príliš často, aby sa nepreplnil vstupný buffer.
- Graphics in Arduino IDE: http://www.idogendel.com/en/archives/489
- https://rheingoldheavy.com/new-arduino-serial-plotter/
Trocha zlozitejsie:
- http://arduino.stackexchange.com/questions/1180/serial-data-plotting-programs
- https://github.com/nprasan/ardugraph
Linearizácia prevodovej charakteristiky
1. Look-up table
#include <avr/pgmspace.h>
const PROGMEM int table[] = {11,12,15,...};
return( table[adcValue] );
Viac info tu: https://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/PROGMEM
2. Po častiach lineárna náhrada
/* segment 1 */
if (adcValue > x0) && (adcValue <= x1)
y = k1 * adcValue + q1;
/* segment 2 */
if (adcValue > x1) && (adcValue <= x2)
y = k2 * adcValue + q2;
return(y)
Dá sa použiť aj funkcia map v Arduine - https://www.arduino.cc/reference/en/language/functions/math/map/
3. Aproximácia funkcie
y = a2 * adcValue^2 + a1 * adcValue + a0;
return(y);
- https://www.gnu.org/software/octave/doc/interpreter/Polynomial-Interpolation.html
- http://octave.sourceforge.net/optim/function/leasqr.html
- http://octave.sourceforge.net/optim/function/expfit.html
- https://www.gnu.org/software/gsl/manual/html_node/Example-programs-for-Nonlinear-Least_002dSquares-Fitting.html
- https://www.gnu.org/software/octave/doc/interpreter/One_002ddimensional-Interpolation.html#One_002ddimensional-Interpolation
Úlohy
Úlohy, ktoré treba odovzdať:
- Graf 1: prevodové charakteristiky
- Chyby podľa EN 60 770
- Nepresnosť
- Meraná chyba
- Nelinearita
- Hysteréza
- Neopakovateľnosť
- Graf 2: chybové krivky (viď obr.)
- Program pre mikroprocesor na linearizáciu
Hodnotenie: 3 body
Deadline: 27. 2. 2018