Acrob030: Rozdiel medzi revíziami
Zo stránky SensorWiki
Nová stránka: Following text will show You a basic connection and operation of the digital compass module. Obrázok:Parallax_HM55B.jpg Product page: [http://www.parallax.com/Store/Sensors/C... |
Bez shrnutí editace |
||
| (2 medziľahlé úpravy od rovnakého používateľa nie sú zobrazené.) | |||
| Riadok 13: | Riadok 13: | ||
[[Obrázok:Parallax_HM55B_Schematic.png]] | [[Obrázok:Parallax_HM55B_Schematic.png]] | ||
Demo program: | Demo program (from the http://arduino.cc/playground/Main/HM55B): | ||
<source lang=" | <source lang="c"> | ||
/* Htachi HM55B Compass by the Pparallax (#29 123) | |||
AUTHOR: kiilo kiilo@kiilo.org | |||
License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/ch/ | |||
http://parallax.com/Store/Microcontrollers/BASICStampModules/tabid/134/txtSearch/hm55b/List/1/ProductID/98/Default.aspx?SortField=ProductName%2cProductName | |||
http://sage.medienkunst.ch/tiki-index.php?page=HowTo_Arduino_Parallax_HM55B_Kompass | |||
http://arduino.cc/playground/HM55B | |||
*/ | |||
#include <math.h> // (no semicolon) | |||
//// VARS | |||
byte EN_pin = 4; | |||
byte CLK_pin = 5; | |||
byte DIO_pin = 6; | |||
int X_Data = 0; | |||
int Y_Data = 0; | |||
int angle; | |||
//// FUNCTIONS | |||
void ShiftOut(int Value, int BitsCount) { | |||
for(int i = BitsCount; i >= 0; i--) { | |||
digitalWrite(CLK_pin, LOW); | |||
if ((Value & 1 << i) == ( 1 << i)) { | |||
digitalWrite(DIO_pin, HIGH); | |||
//Serial.print("1"); | |||
} | |||
else { | |||
digitalWrite(DIO_pin, LOW); | |||
//Serial.print("0"); | |||
} | |||
digitalWrite(CLK_pin, HIGH); | |||
delayMicroseconds(1); | |||
} | |||
//Serial.print(" "); | |||
} | |||
int ShiftIn(int BitsCount) { | |||
int ShiftIn_result; | |||
ShiftIn_result = 0; | |||
pinMode(DIO_pin, INPUT); | |||
for(int i = BitsCount; i >= 0; i--) { | |||
digitalWrite(CLK_pin, HIGH); | |||
delayMicroseconds(1); | |||
if (digitalRead(DIO_pin) == HIGH) { | |||
ShiftIn_result = (ShiftIn_result << 1) + 1; | |||
//Serial.print("x"); | |||
} | |||
else { | |||
ShiftIn_result = (ShiftIn_result << 1) + 0; | |||
//Serial.print("_"); | |||
} | |||
digitalWrite(CLK_pin, LOW); | |||
delayMicroseconds(1); | |||
} | |||
//Serial.print(":"); | |||
// below is difficult to understand: | |||
// if bit 11 is Set the value is negative | |||
// the representation of negative values you | |||
// have to add B11111000 in the upper Byte of | |||
// the integer. | |||
// see: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Two%27s_complement | |||
if ((ShiftIn_result & 1 << 11) == 1 << 11) { | |||
ShiftIn_result = (B11111000 << 8) | ShiftIn_result; | |||
} | |||
return ShiftIn_result; | |||
} | |||
void HM55B_Reset() { | |||
pinMode(DIO_pin, OUTPUT); | |||
digitalWrite(EN_pin, LOW); | |||
ShiftOut(B0000, 3); | |||
digitalWrite(EN_pin, HIGH); | |||
} | |||
void HM55B_StartMeasurementCommand() { | |||
pinMode(DIO_pin, OUTPUT); | |||
digitalWrite(EN_pin, LOW); | |||
ShiftOut(B1000, 3); | |||
digitalWrite(EN_pin, HIGH); | |||
} | |||
int HM55B_ReadCommand() { | |||
int result = 0; | |||
pinMode(DIO_pin, OUTPUT); | |||
digitalWrite(EN_pin, LOW); | |||
ShiftOut(B1100, 3); | |||
result = ShiftIn(3); | |||
return result; | |||
} | |||
void setup() { | |||
Serial.begin(115200); | |||
pinMode(EN_pin, OUTPUT); | |||
pinMode(CLK_pin, OUTPUT); | |||
pinMode(DIO_pin, INPUT); | |||
HM55B_Reset(); | |||
} | |||
void loop() { | |||
HM55B_StartMeasurementCommand(); // necessary!! | |||
delay(40); // the data is 40ms later ready | |||
Serial.print(HM55B_ReadCommand()); // read data and print Status | |||
Serial.print(" "); | |||
X_Data = ShiftIn(11); // Field strength in X | |||
Y_Data = ShiftIn(11); // and Y direction | |||
Serial.print(X_Data); // print X strength | |||
Serial.print(" "); | |||
Serial.print(Y_Data); // print Y strength | |||
Serial.print(" "); | |||
digitalWrite(EN_pin, HIGH); // ok deselect chip | |||
angle = 180 * (atan2(-1 * Y_Data , X_Data) / M_PI); // angle is atan( -y/x) !!! | |||
Serial.print(angle); // print angle | |||
Serial.println(""); | |||
} | |||
</source> | </source> | ||
If the program works correctly, it will send to the serial port (115 200 Bd) following data: | |||
Status Xvalue Yvalue a Azimuth. For example, compass facing NORTH will send following | |||
12 42 0 0 | |||
12 41 -1 1 | |||
12 40 7 -9 | |||
12 40 0 0 | |||
12 40 7 -9 | |||
12 38 0 0 | |||
Demo software: | Demo software (from the http://ozguraytekin.blogspot.com/2010/12/using-hm55b-compass-module-from.html) - run the code below | ||
in the Processing language to obtain the following result: | |||
[[Obrázok:HM55B_ProcessingScreen.png|center]] | |||
<source lang="c"> | |||
// Author: Özgür Aytekin - http://ozguraytekin.blogspot.com | |||
// License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/ch/ | |||
// The Processing serial library allows for easily reading and writing data to and | |||
// from external machines. | |||
// It allows two computers to send and receive data and gives you the flexibility | |||
// to communicate with custom microcontroller devices, using them as the input or | |||
// output to Processing programs. | |||
import processing.serial.*; | |||
// Define variable for receiving data using the communication protocol | |||
Serial serialPort; | |||
// Define variables for storing miscellaneous variables (delivered from arduino) | |||
float hm55bStatus, fieldStrengthInX, fieldStrengthInY, angleRawValue, angleRotateValue = 0; | |||
// Define a variable for storing angle between 0 and 360 degree | |||
float angleDisplayValue = 0; | |||
// Called once when the program is started. | |||
void setup() | |||
{ | |||
// Defines the dimension of the display window in units of pixels. | |||
// The size() function must be the first line in setup(). | |||
size(640, 480); | |||
// Specifies the number of frames to be displayed every second. | |||
// If the processor is not fast enough to maintain the specified rate, | |||
// it will not be achieved. | |||
// For example, the function call frameRate(24) will attempt to refresh 24 times a second. | |||
// It is recommended to set the frame rate within setup(). | |||
// The default rate is 60 frames per second. | |||
frameRate(24); | |||
// Gets a list of all available serial ports. | |||
// Use println() to write the information to the text window. | |||
println(Serial.list()); | |||
// Class for sending and receiving data using the serial communication protocol. | |||
// Constructor Serial(parent, name, rate) | |||
// parent = PApplet: typically use "this", name = String: name of the port (COM1 is the default), | |||
// rate = int: 115200 | |||
serialPort = new Serial(this, Serial.list()[2], 115200); | |||
// Sets a specific byte to buffer until before calling serialEvent(). | |||
// Don't generate a serialEvent() until get a newline character | |||
serialPort.bufferUntil('\n'); | |||
} | |||
// Called when data is available. | |||
void serialEvent(Serial serialPort) | |||
{ | |||
// Reads from the port into a buffer of bytes up to and including a particular character. | |||
// If the character isn't in the buffer, 'null' is returned. | |||
String inputString = serialPort.readStringUntil('\n'); | |||
if (inputString != null) | |||
{ | |||
// Removes whitespace characters from the beginning and end of a String. | |||
// In addition to standard whitespace characters such as space, carriage return, | |||
// and tab, this function also removes the Unicode "nbsp" character. | |||
inputString = trim(inputString); | |||
// The split() function breaks a string into pieces using a character or string as the divider. | |||
// filling substrings into a float array | |||
float[] values = float(split(inputString, " ")); | |||
// we are waiting for four elements | |||
// put the numbers in the values array-variable | |||
if(values.length >= 4) | |||
{ | |||
hm55bStatus = values[0]; | |||
fieldStrengthInX = values[1]; | |||
fieldStrengthInY = values[2]; | |||
angleRawValue = values[3]; | |||
// hm55b is delivering values between 0 and 180 and 0 and -179 | |||
// when the angle value is less than 0, adding 360 to angle | |||
// is delivering the degree between 0 and 359 | |||
if(angleRawValue >= 0 && angleRawValue <= 180) | |||
{ | |||
angleDisplayValue = angleRawValue; | |||
} | |||
else if(angleRawValue < 0) | |||
{ | |||
angleDisplayValue = 360 + angleRawValue; | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | |||
// Called directly after setup() and continuously executes the lines of code contained inside | |||
// its block until the program is stopped or noLoop() is called. | |||
// The draw() function is called automatically and should never be called explicitly. | |||
void draw() | |||
{ | |||
// The background() function sets the color used for the background of the Processing window. | |||
background(200); | |||
// Sets the color used to fill shapes. | |||
fill(153); | |||
print("angleRawValue: "); | |||
print(angleRawValue); | |||
print('\t'); | |||
print("angleDisplayValue: "); | |||
println(angleDisplayValue); | |||
// Re-maps a number from one range to another. | |||
angleRotateValue = map(angleRawValue, 0, 359, 0, PI * 2); | |||
noFill(); | |||
ellipseMode(CENTER); | |||
ellipse(width/2, height/2, 200, 200); | |||
ellipse(width/2, height/2, 20, 20); | |||
text("North", width/2 - 16, 130); | |||
text("South", width/2 - 16, 360); | |||
text("West", 180, height/2); | |||
text("East", 430, height/2); | |||
// Specifies an amount to displace objects within the display window. | |||
// The x parameter specifies left/right translation, | |||
// the y parameter specifies up/down translation, | |||
// and the z parameter specifies translations toward/away from the screen. | |||
translate(width/2, height/2); | |||
// Rotates a shape the amount specified by the angle parameter. | |||
rotate(angleRotateValue); | |||
// Draws a rectangle to the screen. | |||
rect(-6, - 100, 12, 100); | |||
// Forces the program to stop running for a specified time. | |||
delay(500); | |||
} | |||
</source> | |||
[http://forums.parallax.com/showthread.php?78775-Free-graphical-viewer-for-the-Hitachi-HM55B-Compass-Module Download from here...] | [http://forums.parallax.com/showthread.php?78775-Free-graphical-viewer-for-the-Hitachi-HM55B-Compass-Module Download from here...] | ||
| Riadok 26: | Riadok 305: | ||
Arduino page about HM: http://www.arduino.cc/playground/Main/HM55B | Arduino page about HM: http://www.arduino.cc/playground/Main/HM55B | ||
== Theory behind == | |||
What actually measures magnetic sensor? Yes, the strength of the magnetic field. It is just random | |||
coincidence, that current north magnetic pole is near the geographic one. | |||
Also, the Earth magnetic field is very unhomogenous. See picture: | |||
http://netdaw.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/10/solar_wind1.jpg | |||
Also beware of the magnetic inclination and declination... | |||
More: | |||
* http://www.compassdude.com/compass-declination.shtml | |||
* http://earthsci.org/education/fieldsk/declin.htm | |||
* http://www.nationalatlas.gov/articles/geology/a_geomag.html | |||
* Inclination and Declination calculator: <BR> http://ngdc.noaa.gov/geomag/magfield.shtml | |||
You will need Your home coordinations. Determine Your location using Google Maps or GPS. | |||
Tip: how to find lat and lon without the GPS: http://astro.unl.edu/naap/motion1/tc_finding.html | |||
Aktuálna revízia z 13:32, 28. február 2012
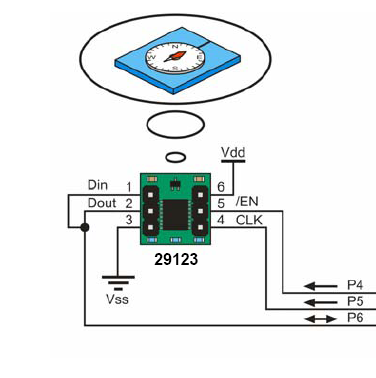
Following text will show You a basic connection and operation of the digital compass module.
Product page: #29123 Hitachi HM55B Compass Module
- Documentation (.pdf)
- Chip datasheet (.pdf)
Schematic diagram:
Demo program (from the http://arduino.cc/playground/Main/HM55B):
/* Htachi HM55B Compass by the Pparallax (#29 123)
AUTHOR: kiilo kiilo@kiilo.org
License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/ch/
http://parallax.com/Store/Microcontrollers/BASICStampModules/tabid/134/txtSearch/hm55b/List/1/ProductID/98/Default.aspx?SortField=ProductName%2cProductName
http://sage.medienkunst.ch/tiki-index.php?page=HowTo_Arduino_Parallax_HM55B_Kompass
http://arduino.cc/playground/HM55B
*/
#include <math.h> // (no semicolon)
//// VARS
byte EN_pin = 4;
byte CLK_pin = 5;
byte DIO_pin = 6;
int X_Data = 0;
int Y_Data = 0;
int angle;
//// FUNCTIONS
void ShiftOut(int Value, int BitsCount) {
for(int i = BitsCount; i >= 0; i--) {
digitalWrite(CLK_pin, LOW);
if ((Value & 1 << i) == ( 1 << i)) {
digitalWrite(DIO_pin, HIGH);
//Serial.print("1");
}
else {
digitalWrite(DIO_pin, LOW);
//Serial.print("0");
}
digitalWrite(CLK_pin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(1);
}
//Serial.print(" ");
}
int ShiftIn(int BitsCount) {
int ShiftIn_result;
ShiftIn_result = 0;
pinMode(DIO_pin, INPUT);
for(int i = BitsCount; i >= 0; i--) {
digitalWrite(CLK_pin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(1);
if (digitalRead(DIO_pin) == HIGH) {
ShiftIn_result = (ShiftIn_result << 1) + 1;
//Serial.print("x");
}
else {
ShiftIn_result = (ShiftIn_result << 1) + 0;
//Serial.print("_");
}
digitalWrite(CLK_pin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(1);
}
//Serial.print(":");
// below is difficult to understand:
// if bit 11 is Set the value is negative
// the representation of negative values you
// have to add B11111000 in the upper Byte of
// the integer.
// see: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Two%27s_complement
if ((ShiftIn_result & 1 << 11) == 1 << 11) {
ShiftIn_result = (B11111000 << 8) | ShiftIn_result;
}
return ShiftIn_result;
}
void HM55B_Reset() {
pinMode(DIO_pin, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(EN_pin, LOW);
ShiftOut(B0000, 3);
digitalWrite(EN_pin, HIGH);
}
void HM55B_StartMeasurementCommand() {
pinMode(DIO_pin, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(EN_pin, LOW);
ShiftOut(B1000, 3);
digitalWrite(EN_pin, HIGH);
}
int HM55B_ReadCommand() {
int result = 0;
pinMode(DIO_pin, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(EN_pin, LOW);
ShiftOut(B1100, 3);
result = ShiftIn(3);
return result;
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(EN_pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(CLK_pin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(DIO_pin, INPUT);
HM55B_Reset();
}
void loop() {
HM55B_StartMeasurementCommand(); // necessary!!
delay(40); // the data is 40ms later ready
Serial.print(HM55B_ReadCommand()); // read data and print Status
Serial.print(" ");
X_Data = ShiftIn(11); // Field strength in X
Y_Data = ShiftIn(11); // and Y direction
Serial.print(X_Data); // print X strength
Serial.print(" ");
Serial.print(Y_Data); // print Y strength
Serial.print(" ");
digitalWrite(EN_pin, HIGH); // ok deselect chip
angle = 180 * (atan2(-1 * Y_Data , X_Data) / M_PI); // angle is atan( -y/x) !!!
Serial.print(angle); // print angle
Serial.println("");
}
If the program works correctly, it will send to the serial port (115 200 Bd) following data: Status Xvalue Yvalue a Azimuth. For example, compass facing NORTH will send following
12 42 0 0 12 41 -1 1 12 40 7 -9 12 40 0 0 12 40 7 -9 12 38 0 0
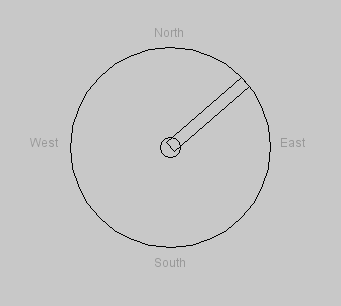
Demo software (from the http://ozguraytekin.blogspot.com/2010/12/using-hm55b-compass-module-from.html) - run the code below in the Processing language to obtain the following result:
// Author: Özgür Aytekin - http://ozguraytekin.blogspot.com
// License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/ch/
// The Processing serial library allows for easily reading and writing data to and
// from external machines.
// It allows two computers to send and receive data and gives you the flexibility
// to communicate with custom microcontroller devices, using them as the input or
// output to Processing programs.
import processing.serial.*;
// Define variable for receiving data using the communication protocol
Serial serialPort;
// Define variables for storing miscellaneous variables (delivered from arduino)
float hm55bStatus, fieldStrengthInX, fieldStrengthInY, angleRawValue, angleRotateValue = 0;
// Define a variable for storing angle between 0 and 360 degree
float angleDisplayValue = 0;
// Called once when the program is started.
void setup()
{
// Defines the dimension of the display window in units of pixels.
// The size() function must be the first line in setup().
size(640, 480);
// Specifies the number of frames to be displayed every second.
// If the processor is not fast enough to maintain the specified rate,
// it will not be achieved.
// For example, the function call frameRate(24) will attempt to refresh 24 times a second.
// It is recommended to set the frame rate within setup().
// The default rate is 60 frames per second.
frameRate(24);
// Gets a list of all available serial ports.
// Use println() to write the information to the text window.
println(Serial.list());
// Class for sending and receiving data using the serial communication protocol.
// Constructor Serial(parent, name, rate)
// parent = PApplet: typically use "this", name = String: name of the port (COM1 is the default),
// rate = int: 115200
serialPort = new Serial(this, Serial.list()[2], 115200);
// Sets a specific byte to buffer until before calling serialEvent().
// Don't generate a serialEvent() until get a newline character
serialPort.bufferUntil('\n');
}
// Called when data is available.
void serialEvent(Serial serialPort)
{
// Reads from the port into a buffer of bytes up to and including a particular character.
// If the character isn't in the buffer, 'null' is returned.
String inputString = serialPort.readStringUntil('\n');
if (inputString != null)
{
// Removes whitespace characters from the beginning and end of a String.
// In addition to standard whitespace characters such as space, carriage return,
// and tab, this function also removes the Unicode "nbsp" character.
inputString = trim(inputString);
// The split() function breaks a string into pieces using a character or string as the divider.
// filling substrings into a float array
float[] values = float(split(inputString, " "));
// we are waiting for four elements
// put the numbers in the values array-variable
if(values.length >= 4)
{
hm55bStatus = values[0];
fieldStrengthInX = values[1];
fieldStrengthInY = values[2];
angleRawValue = values[3];
// hm55b is delivering values between 0 and 180 and 0 and -179
// when the angle value is less than 0, adding 360 to angle
// is delivering the degree between 0 and 359
if(angleRawValue >= 0 && angleRawValue <= 180)
{
angleDisplayValue = angleRawValue;
}
else if(angleRawValue < 0)
{
angleDisplayValue = 360 + angleRawValue;
}
}
}
}
// Called directly after setup() and continuously executes the lines of code contained inside
// its block until the program is stopped or noLoop() is called.
// The draw() function is called automatically and should never be called explicitly.
void draw()
{
// The background() function sets the color used for the background of the Processing window.
background(200);
// Sets the color used to fill shapes.
fill(153);
print("angleRawValue: ");
print(angleRawValue);
print('\t');
print("angleDisplayValue: ");
println(angleDisplayValue);
// Re-maps a number from one range to another.
angleRotateValue = map(angleRawValue, 0, 359, 0, PI * 2);
noFill();
ellipseMode(CENTER);
ellipse(width/2, height/2, 200, 200);
ellipse(width/2, height/2, 20, 20);
text("North", width/2 - 16, 130);
text("South", width/2 - 16, 360);
text("West", 180, height/2);
text("East", 430, height/2);
// Specifies an amount to displace objects within the display window.
// The x parameter specifies left/right translation,
// the y parameter specifies up/down translation,
// and the z parameter specifies translations toward/away from the screen.
translate(width/2, height/2);
// Rotates a shape the amount specified by the angle parameter.
rotate(angleRotateValue);
// Draws a rectangle to the screen.
rect(-6, - 100, 12, 100);
// Forces the program to stop running for a specified time.
delay(500);
}
Arduino page about HM: http://www.arduino.cc/playground/Main/HM55B
Theory behind
What actually measures magnetic sensor? Yes, the strength of the magnetic field. It is just random coincidence, that current north magnetic pole is near the geographic one. Also, the Earth magnetic field is very unhomogenous. See picture:
http://netdaw.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/10/solar_wind1.jpg
Also beware of the magnetic inclination and declination... More:
- http://www.compassdude.com/compass-declination.shtml
- http://earthsci.org/education/fieldsk/declin.htm
- http://www.nationalatlas.gov/articles/geology/a_geomag.html
- Inclination and Declination calculator:
http://ngdc.noaa.gov/geomag/magfield.shtml
You will need Your home coordinations. Determine Your location using Google Maps or GPS.
Tip: how to find lat and lon without the GPS: http://astro.unl.edu/naap/motion1/tc_finding.html