TSL1401 Line Sensor: Rozdiel medzi revíziami
Zo stránky SensorWiki
Bez shrnutí editace |
|||
| (9 medziľahlých úprav od rovnakého používateľa nie je zobrazených.) | |||
| Riadok 9: | Riadok 9: | ||
Dokumenty: | Dokumenty: | ||
* [ | * [https://ams.com/documents/20143/36005/TSL1401CL_DS000136_3-00.pdf Datasheet] | ||
Pripojenie k mikropočítaču Acrob/Arduino: | |||
Napájanie kamery: +5V - Vdd a Zem - GND | |||
Signály: AO (Analog output) - A0 , SI (Start Integration) - D3 a CLK (Clock) - D2 | |||
| Riadok 15: | Riadok 21: | ||
== Úlohy == | == Úlohy == | ||
# Vypočítajte zosilnenie zosilňovača signálu kamery podľa schémy. | |||
# Určte ohniskovú vzdialenosť objektívu | # Určte ohniskovú vzdialenosť objektívu | ||
# Určte vzdialenosť kamery od 3cm pásiku, aby sa premietol na celý čip. | # Určte vzdialenosť kamery od 3cm pásiku, aby sa premietol na celý čip. | ||
| Riadok 27: | Riadok 34: | ||
[[Súbor:TSL1401chip.jpg]] | [[Súbor:TSL1401chip.jpg]] | ||
More info: | |||
* http://arduining.com/2014/03/26/using-the-linear-sensor-array-tsl201r-with-arduino/ | |||
<source lang=c> | <source lang=c> | ||
| Riadok 78: | Riadok 88: | ||
int i; | int i; | ||
int expTime; | int expTime; | ||
delayMicroseconds (1); /* Integration time in microseconds */ | |||
delay(10); /* Integration time in miliseconds */ | |||
digitalWrite (CLKpin, LOW); | digitalWrite (CLKpin, LOW); | ||
| Riadok 84: | Riadok 99: | ||
digitalWrite (SIpin, LOW); | digitalWrite (SIpin, LOW); | ||
delayMicroseconds (1); | delayMicroseconds (1); | ||
/* and now read the real image */ | /* and now read the real image */ | ||
| Riadok 103: | Riadok 118: | ||
} | } | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
Posledný zdroják je vizualizačný program pre Processing.org | |||
<source lang=c> | |||
/* LineViewer --- display for Arduino image sensor 2010-08-01 */ | |||
import processing.serial.*; | |||
final int LINELEN = 128; | |||
final int SCROLLHT = 128; | |||
PImage img; | |||
Serial duino; | |||
boolean Synced = false; | |||
void setup () | |||
{ | |||
println ("<START>"); | |||
println (Serial.list()); | |||
println ("<END>"); | |||
// Open serial port to Arduino at 115200 baud | |||
duino = new Serial (this, Serial.list()[3], 115200); | |||
// Window is same width as sensor, but long enough to scroll | |||
size (LINELEN, SCROLLHT); | |||
// Image is same size as window | |||
img = createImage (LINELEN, SCROLLHT, RGB); | |||
// Initialise image to a shade of blue | |||
img.loadPixels (); | |||
for (int i = 0; i < img.pixels.length; i++) { | |||
img.pixels[i] = color (0, 90, 102); | |||
} | |||
img.updatePixels (); | |||
// Choose image update rate | |||
frameRate (30); | |||
} | |||
void draw () | |||
{ | |||
int i; | |||
int ch; | |||
int nbufs; | |||
int b; | |||
int maxi; | |||
int maxpx; | |||
int mini; | |||
int minpx; | |||
byte[] inbuf = new byte[LINELEN + 1]; | |||
// Synchronise | |||
if (Synced) { | |||
nbufs = duino.available () / (LINELEN + 1); | |||
} | |||
else { | |||
do { | |||
while (duino.available () == 0) | |||
; | |||
ch = duino.read (); | |||
} while (ch != 0); | |||
nbufs = 0; | |||
Synced = true; | |||
} | |||
// Load the image pixels in preparation for next row(s) | |||
img.loadPixels (); | |||
for (b = 0; b < nbufs; b++) { | |||
// Scroll the old image data down the window | |||
for (i = img.pixels.length - LINELEN - 1; i >= 0; i--) { | |||
img.pixels[i + LINELEN] = img.pixels[i]; | |||
} | |||
// Read 128 pixels from image sensor, via Arduino | |||
duino.readBytes (inbuf); | |||
// Check we're still in sync | |||
if (inbuf[128] != 0) { | |||
print ("UNSYNC "); | |||
Synced = false; | |||
} | |||
maxi = 0; | |||
maxpx = 0; | |||
mini = 0; | |||
minpx = 255; | |||
// Transfer incoming pixels to image | |||
for (i = 0; i < LINELEN; i++) { | |||
ch = inbuf[i]; | |||
if (ch < 0) | |||
ch += 256; | |||
if (ch > maxpx) { // Look for brightest pixel | |||
maxi = i; | |||
maxpx = ch; | |||
} | |||
if (ch < minpx) { // Look for brightest pixel | |||
mini = i; | |||
minpx = ch; | |||
} | |||
img.pixels[i] = color (ch, ch, ch); | |||
} | |||
img.pixels[maxi] = color (0, 255, 0); // Mark brightest in green | |||
img.pixels[mini] = color (255, 0, 0); // Mark darkest in red | |||
} | |||
// We're done updating the image, so re-display it | |||
img.updatePixels (); | |||
image (img, 0, 0); | |||
} | |||
</source> | |||
Nová verzia pre Processing 3+ | |||
<source lang="c++"> | |||
/* LineViewer --- display for Arduino image sensor 2019-03-13 */ | |||
import processing.serial.*; | |||
final int LINELEN = 128; | |||
final int SCROLLHT = 128; | |||
PImage img; | |||
Serial duino; | |||
boolean Synced = false; | |||
void settings() | |||
{ | |||
// Window is same width as sensor, but long enough to scroll | |||
size (LINELEN, SCROLLHT); | |||
} | |||
void setup () | |||
{ | |||
println ("<START>"); | |||
println (Serial.list()); | |||
println ("<END>"); | |||
// Open serial port to Arduino at 115200 baud | |||
duino = new Serial (this, Serial.list()[1], 115200); | |||
// Image is same size as window | |||
img = createImage (LINELEN, SCROLLHT, RGB); | |||
// Initialise image to a shade of blue | |||
img.loadPixels (); | |||
for (int i = 0; i < img.pixels.length; i++) { | |||
img.pixels[i] = color (0, 90, 102); | |||
} | |||
img.updatePixels (); | |||
// Choose image update rate | |||
frameRate (30); | |||
} | |||
void draw () | |||
{ | |||
int i; | |||
int ch; | |||
int nbufs; | |||
int b; | |||
int maxi; | |||
int maxpx; | |||
int mini; | |||
int minpx; | |||
byte[] inbuf = new byte[LINELEN + 1]; | |||
// Synchronise | |||
if (Synced) { | |||
nbufs = duino.available () / (LINELEN + 1); | |||
print("s"); | |||
} | |||
else { | |||
print("u"); | |||
do { | |||
while (duino.available () == 0) | |||
; | |||
ch = duino.read (); | |||
} while (ch != 0); | |||
nbufs = 0; | |||
Synced = true; | |||
} | |||
// Load the image pixels in preparation for next row(s) | |||
img.loadPixels (); | |||
for (b = 0; b < nbufs; b++) { | |||
// Scroll the old image data down the window | |||
for (i = img.pixels.length - LINELEN - 1; i >= 0; i--) { | |||
img.pixels[i + LINELEN] = img.pixels[i]; | |||
} | |||
// Read 128 pixels from image sensor, via Arduino | |||
duino.readBytes (inbuf); | |||
print("."); | |||
// Check we're still in sync | |||
if (inbuf[128] != 0) { | |||
print ("UNSYNC "); | |||
Synced = false; | |||
} | |||
maxi = 0; | |||
maxpx = 0; | |||
mini = 0; | |||
minpx = 255; | |||
// Transfer incoming pixels to image | |||
for (i = 0; i < LINELEN; i++) { | |||
ch = inbuf[i]; | |||
if (ch < 0) | |||
ch += 256; | |||
if (ch > maxpx) { // Look for brightest pixel | |||
maxi = i; | |||
maxpx = ch; | |||
} | |||
if (ch < minpx) { // Look for brightest pixel | |||
mini = i; | |||
minpx = ch; | |||
} | |||
img.pixels[i] = color (ch, ch, ch); | |||
} | |||
img.pixels[maxi] = color (0, 255, 0); // Mark brightest in green | |||
img.pixels[mini] = color (255, 0, 0); // Mark darkest in red | |||
} | |||
// We're done updating the image, so re-display it | |||
img.updatePixels (); | |||
print("."); | |||
image (img, 0, 0); | |||
} | |||
</source> | |||
[[MEMS inteligentné senzory a aktuátory#Cvi.C4.8Denia|Návrat na zoznam cvičení...]] | |||
[[Category:MEMS]] | |||
Aktuálna revízia z 09:41, 22. marec 2020
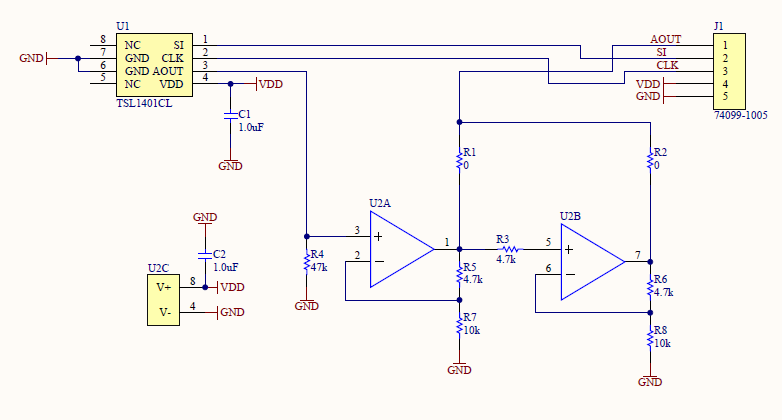
Základom kamery je lineárne senzorové pole 128x1 doplnené o vzorkovací obvod. Funkcia je popísaná v datasheete. Kamera okrem toho obsahuje oddelovací zosilňovač, ktorého schéma zapojenia je tu:
Dokumenty:
Pripojenie k mikropočítaču Acrob/Arduino:
Napájanie kamery: +5V - Vdd a Zem - GND
Signály: AO (Analog output) - A0 , SI (Start Integration) - D3 a CLK (Clock) - D2
Úlohy
- Vypočítajte zosilnenie zosilňovača signálu kamery podľa schémy.
- Určte ohniskovú vzdialenosť objektívu
- Určte vzdialenosť kamery od 3cm pásiku, aby sa premietol na celý čip.
- Pomocou osciloskopu a čierneho pásiku zaostrite kameru
- Zistite vplyv osvetlenia zadnej steny čipu na kvalitu obrazu
- Pripojte kameru k PC a pomocou demonštračného programu zosnímajte jednoduchý čiarový kód
- Pozrite si zároveň aj signál na osciloskope (uložte na USB klúč)
- Zistite vplyv zmeny expozičnej doby na kvalitu snímky
- Zosnímajte predložený čiarový kód.
- Záznam z každej úlohy vypracujte vo forme technickej správy.
More info:
/* ************************************************************ */
/* Cvicenie so snimacom TSL1401 -- riadkovy CMOS snimac 128px */
/* */
/* ************************************************************ */
// Sensor interface:
#define AOpin 0 // Analog output - yellow
#define SIpin 3 // Start Integration - orange
#define CLKpin 2 // Clock - red
// Vcc - brown
// GND - black
#define NPIXELS 128 // No. of pixels in array
byte Pixel[NPIXELS]; // Field for measured values <0-255>
#define FASTADC 1
// defines for setting and clearing register bits
#define cbi(sfr, bit) (_SFR_BYTE(sfr) &= ~_BV(bit))
#define sbi(sfr, bit) (_SFR_BYTE(sfr) |= _BV(bit))
void setup(void)
{
pinMode(SIpin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(CLKpin, OUTPUT);
//pinMode (AOpin, INPUT);
digitalWrite(SIpin, LOW); // IDLE state
digitalWrite(CLKpin, LOW); // IDLE state
#if FASTADC
// set prescale to 16
sbi(ADCSRA,ADPS2);
cbi(ADCSRA,ADPS1);
cbi(ADCSRA,ADPS0);
#endif
Serial.begin (115200);
}
void loop (void)
{
int i;
int expTime;
delayMicroseconds (1); /* Integration time in microseconds */
delay(10); /* Integration time in miliseconds */
digitalWrite (CLKpin, LOW);
digitalWrite (SIpin, HIGH);
digitalWrite (CLKpin, HIGH);
digitalWrite (SIpin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds (1);
/* and now read the real image */
for (i = 0; i < NPIXELS; i++) {
Pixel[i] = analogRead (AOpin)/4 ; // 8-bit is enough
digitalWrite (CLKpin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds (1);
digitalWrite (CLKpin, HIGH);
}
Serial.write ((byte)0); // sync byte = 0
for (i = 0; i < NPIXELS; i++) {
Serial.write ((byte)Pixel[i]+1);
}
}
Posledný zdroják je vizualizačný program pre Processing.org
/* LineViewer --- display for Arduino image sensor 2010-08-01 */
import processing.serial.*;
final int LINELEN = 128;
final int SCROLLHT = 128;
PImage img;
Serial duino;
boolean Synced = false;
void setup ()
{
println ("<START>");
println (Serial.list());
println ("<END>");
// Open serial port to Arduino at 115200 baud
duino = new Serial (this, Serial.list()[3], 115200);
// Window is same width as sensor, but long enough to scroll
size (LINELEN, SCROLLHT);
// Image is same size as window
img = createImage (LINELEN, SCROLLHT, RGB);
// Initialise image to a shade of blue
img.loadPixels ();
for (int i = 0; i < img.pixels.length; i++) {
img.pixels[i] = color (0, 90, 102);
}
img.updatePixels ();
// Choose image update rate
frameRate (30);
}
void draw ()
{
int i;
int ch;
int nbufs;
int b;
int maxi;
int maxpx;
int mini;
int minpx;
byte[] inbuf = new byte[LINELEN + 1];
// Synchronise
if (Synced) {
nbufs = duino.available () / (LINELEN + 1);
}
else {
do {
while (duino.available () == 0)
;
ch = duino.read ();
} while (ch != 0);
nbufs = 0;
Synced = true;
}
// Load the image pixels in preparation for next row(s)
img.loadPixels ();
for (b = 0; b < nbufs; b++) {
// Scroll the old image data down the window
for (i = img.pixels.length - LINELEN - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
img.pixels[i + LINELEN] = img.pixels[i];
}
// Read 128 pixels from image sensor, via Arduino
duino.readBytes (inbuf);
// Check we're still in sync
if (inbuf[128] != 0) {
print ("UNSYNC ");
Synced = false;
}
maxi = 0;
maxpx = 0;
mini = 0;
minpx = 255;
// Transfer incoming pixels to image
for (i = 0; i < LINELEN; i++) {
ch = inbuf[i];
if (ch < 0)
ch += 256;
if (ch > maxpx) { // Look for brightest pixel
maxi = i;
maxpx = ch;
}
if (ch < minpx) { // Look for brightest pixel
mini = i;
minpx = ch;
}
img.pixels[i] = color (ch, ch, ch);
}
img.pixels[maxi] = color (0, 255, 0); // Mark brightest in green
img.pixels[mini] = color (255, 0, 0); // Mark darkest in red
}
// We're done updating the image, so re-display it
img.updatePixels ();
image (img, 0, 0);
}
Nová verzia pre Processing 3+
/* LineViewer --- display for Arduino image sensor 2019-03-13 */
import processing.serial.*;
final int LINELEN = 128;
final int SCROLLHT = 128;
PImage img;
Serial duino;
boolean Synced = false;
void settings()
{
// Window is same width as sensor, but long enough to scroll
size (LINELEN, SCROLLHT);
}
void setup ()
{
println ("<START>");
println (Serial.list());
println ("<END>");
// Open serial port to Arduino at 115200 baud
duino = new Serial (this, Serial.list()[1], 115200);
// Image is same size as window
img = createImage (LINELEN, SCROLLHT, RGB);
// Initialise image to a shade of blue
img.loadPixels ();
for (int i = 0; i < img.pixels.length; i++) {
img.pixels[i] = color (0, 90, 102);
}
img.updatePixels ();
// Choose image update rate
frameRate (30);
}
void draw ()
{
int i;
int ch;
int nbufs;
int b;
int maxi;
int maxpx;
int mini;
int minpx;
byte[] inbuf = new byte[LINELEN + 1];
// Synchronise
if (Synced) {
nbufs = duino.available () / (LINELEN + 1);
print("s");
}
else {
print("u");
do {
while (duino.available () == 0)
;
ch = duino.read ();
} while (ch != 0);
nbufs = 0;
Synced = true;
}
// Load the image pixels in preparation for next row(s)
img.loadPixels ();
for (b = 0; b < nbufs; b++) {
// Scroll the old image data down the window
for (i = img.pixels.length - LINELEN - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
img.pixels[i + LINELEN] = img.pixels[i];
}
// Read 128 pixels from image sensor, via Arduino
duino.readBytes (inbuf);
print(".");
// Check we're still in sync
if (inbuf[128] != 0) {
print ("UNSYNC ");
Synced = false;
}
maxi = 0;
maxpx = 0;
mini = 0;
minpx = 255;
// Transfer incoming pixels to image
for (i = 0; i < LINELEN; i++) {
ch = inbuf[i];
if (ch < 0)
ch += 256;
if (ch > maxpx) { // Look for brightest pixel
maxi = i;
maxpx = ch;
}
if (ch < minpx) { // Look for brightest pixel
mini = i;
minpx = ch;
}
img.pixels[i] = color (ch, ch, ch);
}
img.pixels[maxi] = color (0, 255, 0); // Mark brightest in green
img.pixels[mini] = color (255, 0, 0); // Mark darkest in red
}
// We're done updating the image, so re-display it
img.updatePixels ();
print(".");
image (img, 0, 0);
}